T2-Weighted MRI Images
T2-weighted MRI images are a fundamental component of medical imaging, renowned for their ability to highlight fluid-rich areas within the body. This imaging sequence provides detailed visuals of tissues with high water content, making diagnosing a wide range of conditions essential. Its ability to distinguish between normal and pathological tissues is critical for accurate medical assessments and treatment planning.
Importance of T2-weighted images in identifying fluid-rich tissues
T2-weighted images detect and evaluate tissues with increased water content, such as cerebrospinal fluid, joint effusions, and edema. Fluids appear bright on T2-weighted scans, providing a stark contrast against darker surrounding tissues. This capability makes T2 imaging particularly valuable for identifying conditions like inflammation, infections, cysts, and tumors with necrotic or fluid-filled centers. By highlighting these fluid-rich areas, T2-weighted MRI is pivotal in pinpointing pathological changes that might go unnoticed.
How T2-Weighted MRI Images Work
T2-weighted MRI images are generated by measuring protons’ transverse relaxation time (T2) within tissues. When a radiofrequency pulse disrupts the alignment of protons in the body’s magnetic field, these protons lose coherence at varying rates depending on the tissue’s water content. This dephasing rate determines the signal intensity captured during the scan, resulting in the distinct contrast seen in T2-weighted images.
Tissues with high water content, such as cerebrospinal fluid, edema, and inflammatory sites, retain their signal longer and appear bright on T2-weighted scans. Conversely, tissues with lower water content, like fat and dense structures, lose their signal more quickly and appear darker. This property makes T2-weighted imaging highly sensitive to fluid-rich areas and invaluable for identifying pathological changes, such as swelling, infections, and lesions.
What T2-Weighted MRI Images Show
T2-weighted MRI images are known for highlighting fluid-filled and water-rich tissues in the body. This imaging sequence is essential for identifying pathological changes involving increased water content, providing valuable insights for diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions by offering a clear contrast between normal and abnormal tissues, T2-weighted imaging aids in the precise localization and characterization of lesions.
Fluid contrast and its diagnostic significance
The hallmark of T2-weighted imaging is its sensitivity to water content, with fluids appearing bright on the scan. This contrast is beneficial for visualizing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), joint effusions, and other fluid accumulations. The bright signal intensity makes detecting abnormalities like swelling, inflammation, or fluid-filled spaces easier. This capability is vital for diagnosing hydrocephalus, soft tissue infections, and organ inflammation.
Examples of common findings, such as cysts, edema, and infections
T2-weighted MRI images frequently detect cysts, which appear as bright, fluid-filled structures with distinct boundaries. Edema, a common sign of tissue injury or inflammation, is easily visualized due to its high water content. Similarly, infections such as abscesses or inflammatory processes show up clearly because of the fluid-rich nature of these pathological changes. T2-weighted imaging is also invaluable in detecting joint effusions, synovitis, and other fluid-related abnormalities, ensuring accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
Applications of T2-Weighted MRI in Diagnosis
T2-weighted MRI images are critical in diagnosing various conditions across multiple medical fields. Their ability to highlight fluid-rich tissues makes them a versatile tool for detecting pathological changes, aiding clinicians in identifying and managing diseases effectively.
Neurological applications: T2-weighted imaging is invaluable in neurology for its sensitivity to fluid and inflammation. It is commonly used to detect brain lesions, such as those caused by multiple sclerosis, strokes, or tumors with necrotic centers. Bright signals from edema or inflamed areas help identify acute or chronic injuries. Additionally, T2 imaging provides crucial insights into cerebrospinal fluid abnormalities, aiding in diagnosing hydrocephalus, meningitis, or cysts in the brain and spine.
Musculoskeletal evaluations: In musculoskeletal imaging, T2-weighted scans are ideal for assessing soft tissue injuries and fluid-related abnormalities. Joint effusions, which appear bright due to their high water content, can be easily detected. T2 imaging also identifies tendon tears, ligament damage, and muscle edema caused by trauma or overuse. Furthermore, it is an effective tool for evaluating infections, inflammatory conditions like synovitis, and soft tissue tumors.
Abdominal and pelvic imaging: T2-weighted imaging is widely used in abdominal and pelvic diagnostics due to its ability to highlight water-rich structures and abnormalities. Organs like the liver, kidneys, and bladder are well-visualized, allowing for the detection of cysts, abscesses, or tumors. It is also effective in identifying fluid accumulation, such as ascites or pelvic inflammatory disease. The detailed contrast in T2-weighted images provides clinicians with essential information for diagnosing and managing complex abdominal and pelvic conditions.
Have an MRI report? Get a second opinion from top radiology experts. 👉 Upload your MRI for a comprehensive analysis today.
Advantages of T2-Weighted MRI Images
T2-weighted MRI images offer unique benefits that make them essential for medical diagnostics. Their ability to highlight fluid-rich tissues and pathological changes provides critical insights, enabling accurate diagnoses across various specialties. Below are the two key advantages of T2-weighted imaging.
High sensitivity to pathological changes
T2-weighted imaging is highly sensitive to abnormalities associated with increased water content, such as edema, inflammation, and infections. Bright signals in fluid-rich areas allow for detecting subtle changes in tissues that may not be visible in other imaging sequences. This sensitivity is particularly valuable in identifying acute injuries, inflammatory processes, and fluid-filled cysts, making T2-weighted scans indispensable for early and precise diagnosis.
Versatility in diagnosing diverse medical conditions
The versatility of T2-weighted MRI images lies in their ability to diagnose various conditions across different organ systems. From neurological issues like brain lesions and spinal abnormalities to musculoskeletal injuries such as tendon tears and joint effusions, T2-weighted imaging provides detailed information for effective treatment planning. Additionally, its application in abdominal and pelvic imaging, which detects cysts, abscesses, and fluid accumulation, demonstrates its adaptability in addressing diverse medical challenges. This broad utility makes T2-weighted MRI a cornerstone of diagnostic imaging.
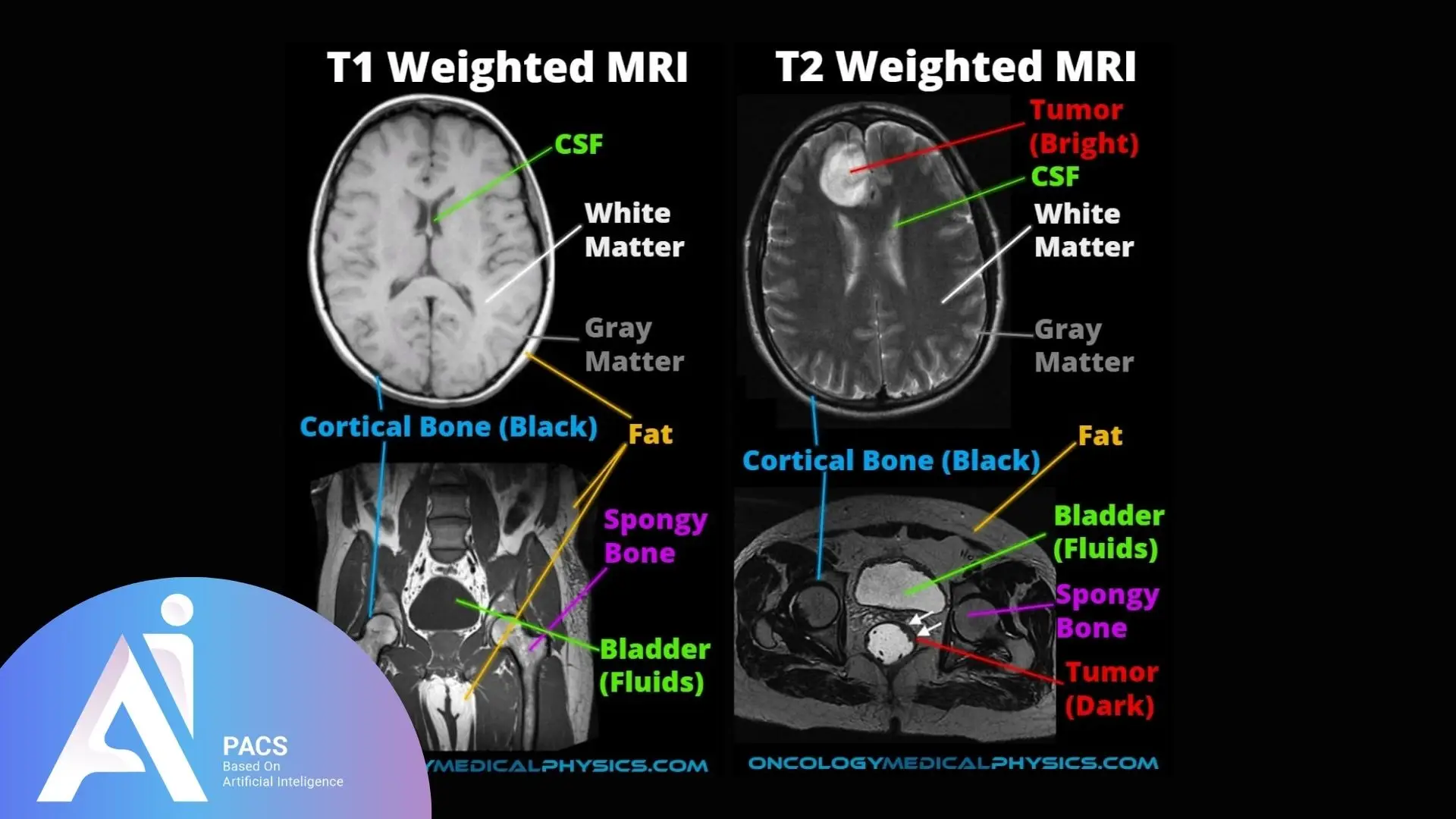
Comparison Between T2 and T1-Weighted Images
T2-weighted and T1-weighted MRI images are complementary in medical imaging, differing primarily in their tissue contrast and diagnostic applications.
- T2-Weighted Images highlight water content, with fluids appearing bright. They are ideal for detecting edema, inflammation, and fluid-filled abnormalities like cysts and infections.
- T1-Weighted Images emphasize fat content, with fat appearing bright and fluids dark. They excel in visualizing anatomical structures and are often used with contrast agents for enhanced imaging of tumors and vascular abnormalities.
These sequences provide a comprehensive view, aiding in accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment planning.
Looking for insights on how T1-weighted MRI images assist in identifying brain and spinal cord conditions? Explore this in-depth look at T1-weighted MRI
Understanding Common T2-Weighted MRI Findings
T2-weighted MRI images are valuable for identifying and understanding various medical conditions. Thanks to their ability to differentiate between fluid-rich and solid tissues, clinicians can accurately interpret pathological changes and abnormalities in the body by analyzing the bright and dark regions in these images.
Interpreting bright and dark regions in images
In T2-weighted images, bright regions typically indicate areas with high water content, such as cerebrospinal fluid, joint effusions, or inflamed tissues. This bright signal makes identifying abnormalities like edema, cysts, or infections easier. Conversely, darker regions represent tissues with lower water content, such as fat, dense muscle, or bone. This contrast helps distinguish between normal anatomical structures and areas of concern, facilitating precise diagnosis.
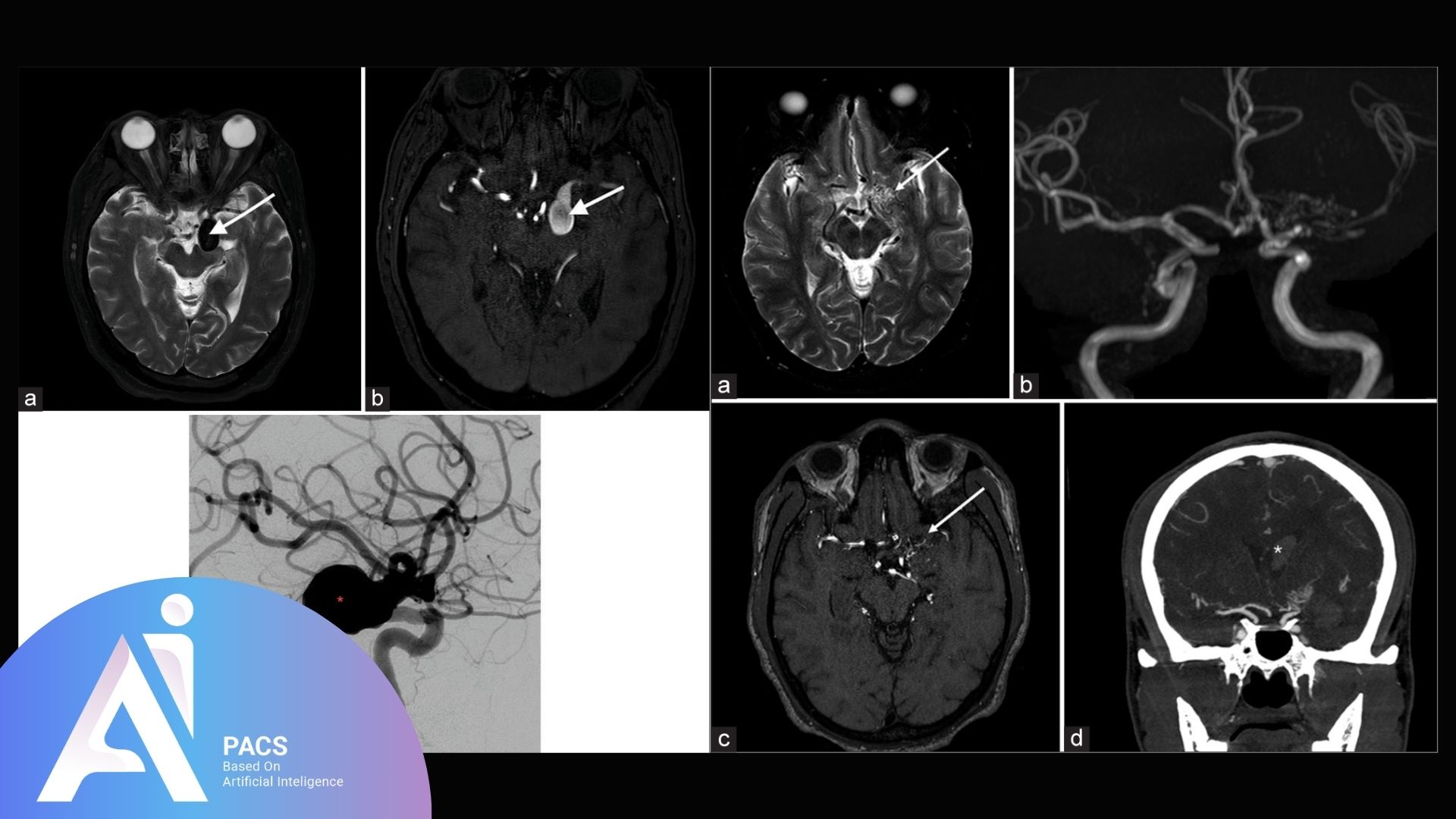
Case examples of typical pathologies visualized with T2 imaging
T2-weighted imaging is commonly used to detect:
- Edema and Inflammation: Bright signals indicate swelling due to injury or infection.
- Cysts: These fluid-filled structures appear bright with well-defined borders.
- Tumors: Necrotic or fluid-filled components of tumors are easily visualized.
- Infections: Abscesses or inflamed tissues are highlighted due to their fluid content.
- Joint Effusions: Fluid accumulation in joints is readily apparent on T2 scans.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and importance of T2-weighted imaging in diagnosing a wide range of conditions.
Conclusion
T2-weighted MRI images are a powerful diagnostic tool, offering unparalleled sensitivity to fluid-rich tissues and pathological changes. Their ability to highlight abnormalities such as edema, inflammation, cysts, and infections makes them indispensable across various medical specialties. By providing detailed insights into normal and abnormal structures, T2-weighted imaging plays a crucial role in early diagnosis and effective treatment planning. With advancements in MRI technology, the versatility and precision of T2-weighted imaging continue to enhance patient care, solidifying its place in modern medicine.
Get professional advice on your T2-weighted MRI results. 👉 Submit your report here for expert review.