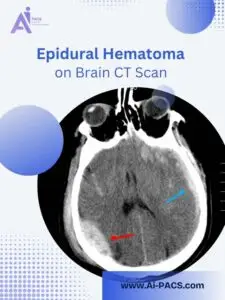
Key Indicators in a Brain CT Scan
Tissue Density
In a CT scan, different tissues have varying densities. Bones, due to their high density, appear bright white, whereas softer tissues such as the brain appear in shades of gray or black.
If you want to understand how density variations appear in other types of imaging, you can read Comprehensive Guide to T2-Weighted MRI Images and Their Diagnostic Insights and Understanding T1-Weighted MRI Images and Their Diagnostic Value. These guides explain how tissue contrast helps radiologists identify abnormalities in MRI scans.
Presence of Hemorrhage or Clots
One of the most critical indicators, particularly in cases like epidural hematoma, is the presence of hemorrhage or blood clots, which typically appear as bright white areas.
Brain Swelling or Edema
If the brain undergoes swelling or edema, it may lead to changes in the shape and size of the brain’s ventricles and an increase in intracranial pressure, which is visible on a CT scan.
📄 Want Fast, Expert Interpretation of Your Brain CT?
When dealing with critical signs like hemorrhage or swelling, timing and accuracy matter. With AI-PACS’s Online CT Scan Reporting Services, experienced radiologists deliver reliable interpretations remotely—so you don’t lose time waiting.
Conditions Evaluated with Brain CT Scan
This imaging technique allows physicians to obtain detailed insights into the brain’s internal structures and diagnose various medical conditions. Some of the key conditions assessed using CT scans include:
- Stroke: Rapid identification of a stroke, determining its type (ischemic or hemorrhagic), and assessing the extent of brain tissue damage.
- Brain Tumors: Detection and evaluation of the size, location, and type of brain tumors.
- Head Injuries from trauma: Assessment of skull fractures, internal bleeding, and trauma-induced brain damage.
- Aneurysms: Identification of abnormal bulging in brain blood vessels.
- Brain Infections: Diagnosis of brain abscesses, encephalitis, and other infections affecting the central nervous system.
- Hydrocephalus: Evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulation and identifying obstructions in CSF flow pathways.
- Epilepsy: Detection of structural abnormalities that may contribute to seizures.
- Brain Abscesses: Identification and evaluation of pus-filled infections within the brain tissue.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Assessment of degenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
- Vascular Disorders: Detection of vascular abnormalities, including arterial narrowing and venous malformations.
- Developmental Disorders: Evaluation of congenital abnormalities and developmental brain disorders.
The use of CT scans enables physicians to diagnose brain-related conditions with greater accuracy, allowing for appropriate treatment planning and intervention. However, CT scans expose patients to ionizing radiation, making MRI a preferred option in certain situations where repeated imaging is necessary, particularly for younger patients or pregnant women. Compared to MRI, CT scans provide faster imaging and are particularly effective in detecting acute conditions such as hemorrhages and fractures. However, MRI offers superior soft tissue contrast and is more useful for detecting conditions like multiple sclerosis or subtle brain lesions. The choice between CT and MRI depends on the clinical scenario and the specific diagnostic needs of the patient.
Common Terms in Brain CT Scan Reports
Interpreting a brain CT scan requires familiarity with terms that describe specific findings and characteristics. Below are some commonly used terms:
- Hypodense: An area with lower density than normal brain tissue, often indicating stroke, injury, or non-neoplastic masses.
- Hyperdense: An area with higher density than normal brain tissue, commonly associated with hemorrhage, calcium deposits, or certain tumors.
- Edema: Swelling and fluid accumulation in brain tissue, often appearing as a hypodense region.
- Hemorrhage: Internal bleeding within the brain, typically appearing as hyperdense areas.
- Hematoma: A localized collection of blood within the brain, which may appear hyperdense or isodense depending on the stage of hemorrhage.
- Atrophy: Reduction in brain tissue volume, often seen as an enlargement of CSF-filled spaces, such as ventricles and sulci.
- Hydrocephalus: An increase in cerebrospinal fluid volume, leading to ventricular enlargement.
- Lesion: Any abnormality that may represent a tumor, injury, or inflammatory process.
- Calcification: Calcium deposition in brain tissues, often appearing as hyperdense regions.
- Isodense: An area with a density similar to normal brain tissue, sometimes observed in tumors or other lesions.
- Arterial Occlusion: Blockage of a cerebral artery, potentially leading to a stroke.
- Subarachnoid Space: The area between the arachnoid and pia mater layers of the brain, filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Understanding these neurological terms is essential, but expert brain CT interpretation provides the clinical context and significance of findings specific to your neurological health and symptoms.
📄 Want to See How Real Brain CT Reports Look?
Reading about terms like “hypodense” or “edema” is helpful—but seeing how they’re described in actual medical reports offers much more clarity. Explore our CT Scan Report Format Guide to learn how brain findings are documented by radiologists in real-world settings.
Next Steps After a CT Scan
What Patients Should Expect
Once a brain CT scan is completed, the next step is consulting a neurologist or a specialist for a thorough review and interpretation of the findings. Based on the results, the physician may identify signs of hemorrhage, tumors, stroke, or other brain abnormalities.
Depending on the diagnosis, the recommended treatment may include medications, surgical intervention, or lifestyle modifications. In emergency cases, such as acute hemorrhage or increased intracranial pressure, immediate medical intervention may be necessary. If further assessment is necessary, additional imaging techniques such as MRI scans may be requested for a more detailed evaluation of brain structures and functions. These steps ensure the most accurate diagnosis and the best possible treatment plan.
Brain CT interpretation requires specialized neuroimaging report expertise. Whether you’re dealing with emergency findings, follow-up imaging, or concerning neurological symptoms, professional radiological consultation can provide crucial insights into your brain health and help guide appropriate medical decisions.
Who Should Get a Second Opinion for a Brain CT Scan?
If you’ve had a brain CT scan and still feel unsure about your diagnosis, you’re not alone—and getting a second opinion might be the smartest next step. People dealing with ongoing headaches, memory problems, dizziness, unexplained neurological symptoms, or changes after a head injury often benefit from having their scans reviewed by a second expert. Sometimes, the original report may be vague or miss subtle findings that could change the course of treatment. A fresh look by a specialist in brain imaging can provide peace of mind, catch what others may have missed, and guide you toward the right next test—whether that’s a follow-up CT, an MRI, or something else. This is especially important when multiple doctors give conflicting advice or when your symptoms don’t match the report.
If you’re curious about your imaging results or need expert advice on which test is right, don’t hesitate to contact us for a professional radiology consultation.
Final Thoughts
Interpreting a brain CT scan requires specialized medical expertise that only trained professionals possess. While understanding the basic principles can help patients become more familiar with their imaging results, a precise diagnosis and treatment decisions should always be made by a medical expert.
Accuracy in medical diagnosis is of utmost importance, and professional medical consultation should never be overlooked. Every CT scan offers a crucial window into brain health, helping detect potential issues early. If abnormalities are found, follow-up imaging or urgent medical intervention may be necessary. While understanding the basics can be helpful, precise interpretation and treatment should always be entrusted to medical professionals. Consult your specialist to ensure an accurate diagnosis and the best possible care for your health. Trust your healthcare provider for the most reliable interpretation of your results.
Your brain imaging results deserve expert attention. 👉 Upload your brain CT scan report to AI-PACS for a detailed second opinion from certified radiologists.
You can also continue reading Alzheimer’s Disease: Why, When, and Who Should Consider Brain Imaging or Cerebellopontine Angle (CP Angle) Lesions – Why, When, and Who Should Consider Medical Imaging to learn more about how imaging supports early detection and accurate diagnosis of neurological disorders.
References: