What Are Pituitary Adenomas?
Pituitary adenomas are benign tumors that develop in the pituitary gland, a vital structure located at the base of the brain, responsible for regulating hormones. These tumors are classified into microadenomas (less than 10 mm in diameter) and macroadenomas (10 mm or larger). While microadenomas are often managed with medication, macroadenomas may require surgery due to their size and potential pressure effects on nearby structures.
Pituitary Adenomas MRI is the only way to diagnose the tumor, especially the micro ones.
High prolactin levels (hyperprolactinemia) are a common finding in some pituitary adenomas, leading to hormonal imbalances. In contrast, larger tumors may exert pressure effects, causing symptoms such as vision disturbances and headaches. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, and dynamic MRI plays a key role in identifying these tumors.
👉 Upload your MRI report now for an expert review with AI-PACS and get the clarity you need to move forward confidently.
Why Is Medical Imaging Needed for Pituitary Adenomas?
Medical imaging is essential for diagnosing and monitoring pituitary adenomas due to several reasons:
- Accurate Diagnosis: MRI, particularly dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI, provides detailed tumor images, aiding in precise diagnosis.
- Assessment of Compression Effects: Macroadenomas can compress the optic chiasm (the point where the optic nerves cross), leading to visual field loss. Imaging helps determine the extent of compression.
- Hormonal Dysfunction Evaluation: Some adenomas, especially prolactinomas, cause hormone imbalances, which can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life.
- Treatment Planning: Imaging helps differentiate between tumors that can be managed with medication (such as prolactinomas) and those requiring surgical intervention (such as non-secreting macroadenomas).
When Should Medical Imaging Be Used for Pituitary Adenomas?
When should you get a pituitary adenoma MRI?
Medical imaging should be considered in the following situations:
Presence of Symptoms:
- Persistent headaches
- Vision changes, including tunnel vision or double vision
- Symptoms of hormonal imbalance, such as irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, or unexplained weight gain/loss
Elevated Hormone Levels:
- High prolactin levels (suggesting a prolactinoma)
- Abnormal cortisol, growth hormone, or thyroid hormone levels
Failure to Respond to Medical Treatment: If a patient with a known pituitary adenoma does not respond to medication, imaging is necessary to reassess tumor size and progression.
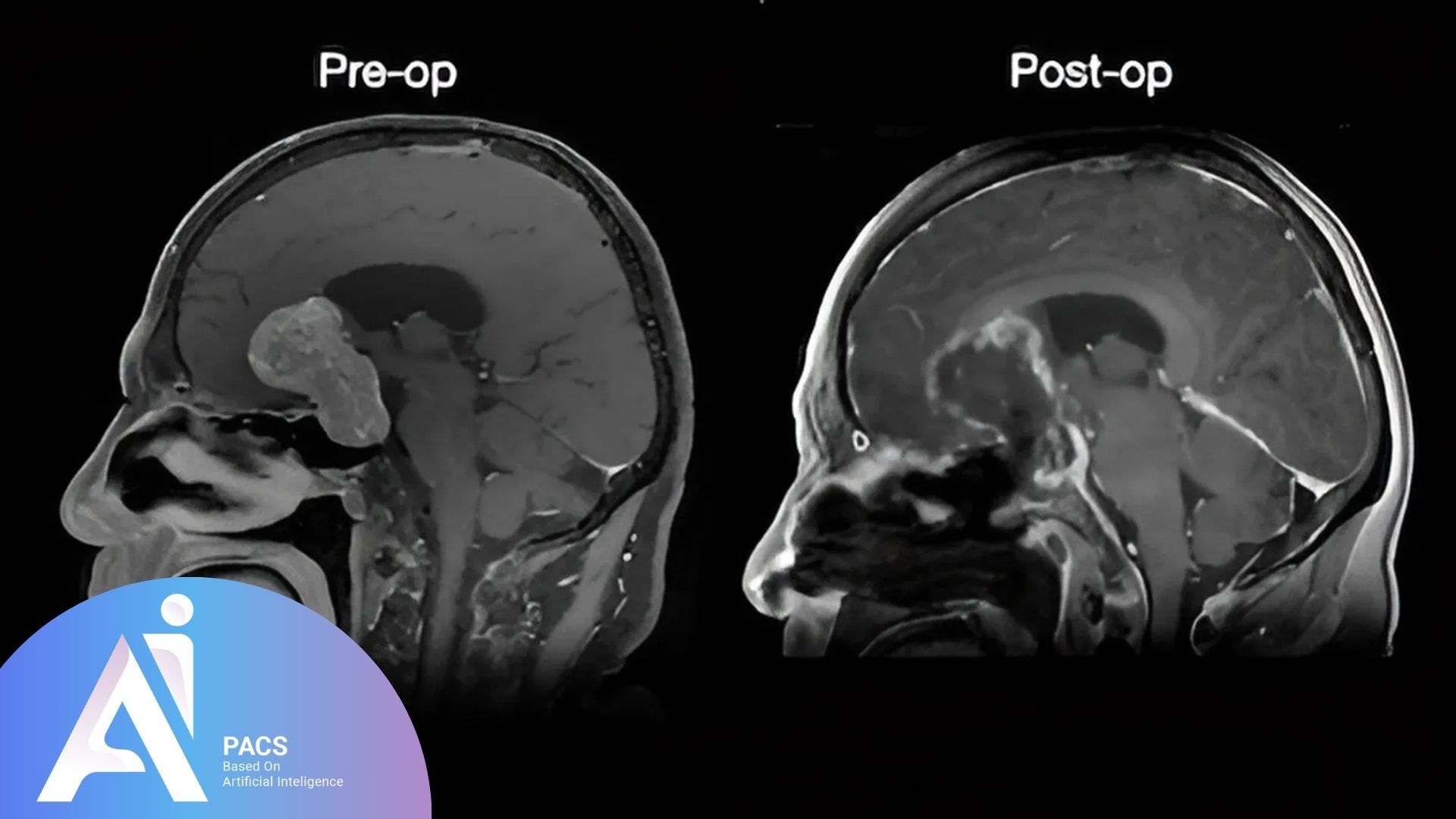
Preoperative and Postoperative Assessment: MRI is crucial both before and after pituitary tumor surgery to evaluate tumor removal and detect residual tissue.
Who Needs Imaging and an Expert Consultation?
Certain patients benefit the most from pituitary imaging:
- Patients with Progressive Symptoms: Individuals experiencing worsening vision, chronic headaches, or neurological symptoms should undergo imaging immediately.
- Patients with Known Pituitary Tumors: Those diagnosed with a microadenoma or macroadenoma require routine follow-ups through MRI to monitor growth and hormone activity.
- Patients with Large Macroadenomas Affecting Nearby Structures: Some macroadenomas grow large enough to extend into the cavernous sinus (a large vein at the base of the brain that contains major arteries and important nerves controlling eye movement). If the tumor invades this area, it can affect the carotid arteries (major blood vessels supplying the brain) and cranial nerves (nerves responsible for eye movements and facial sensation). Imaging is crucial in determining the extent of involvement.
- Individuals Who Have Undergone Surgery and Require Further Evaluation: In some cases, patients who have already had surgery may need a second procedure if part of the tumor remains. Follow-up imaging ensures that tumor regrowth or complications are appropriately assessed before treatment decisions are made.
- Individuals Seeking a Second Opinion: Consulting an expert radiologist or endocrinologist for complex or unclear cases ensures an accurate diagnosis and optimal treatment plan.
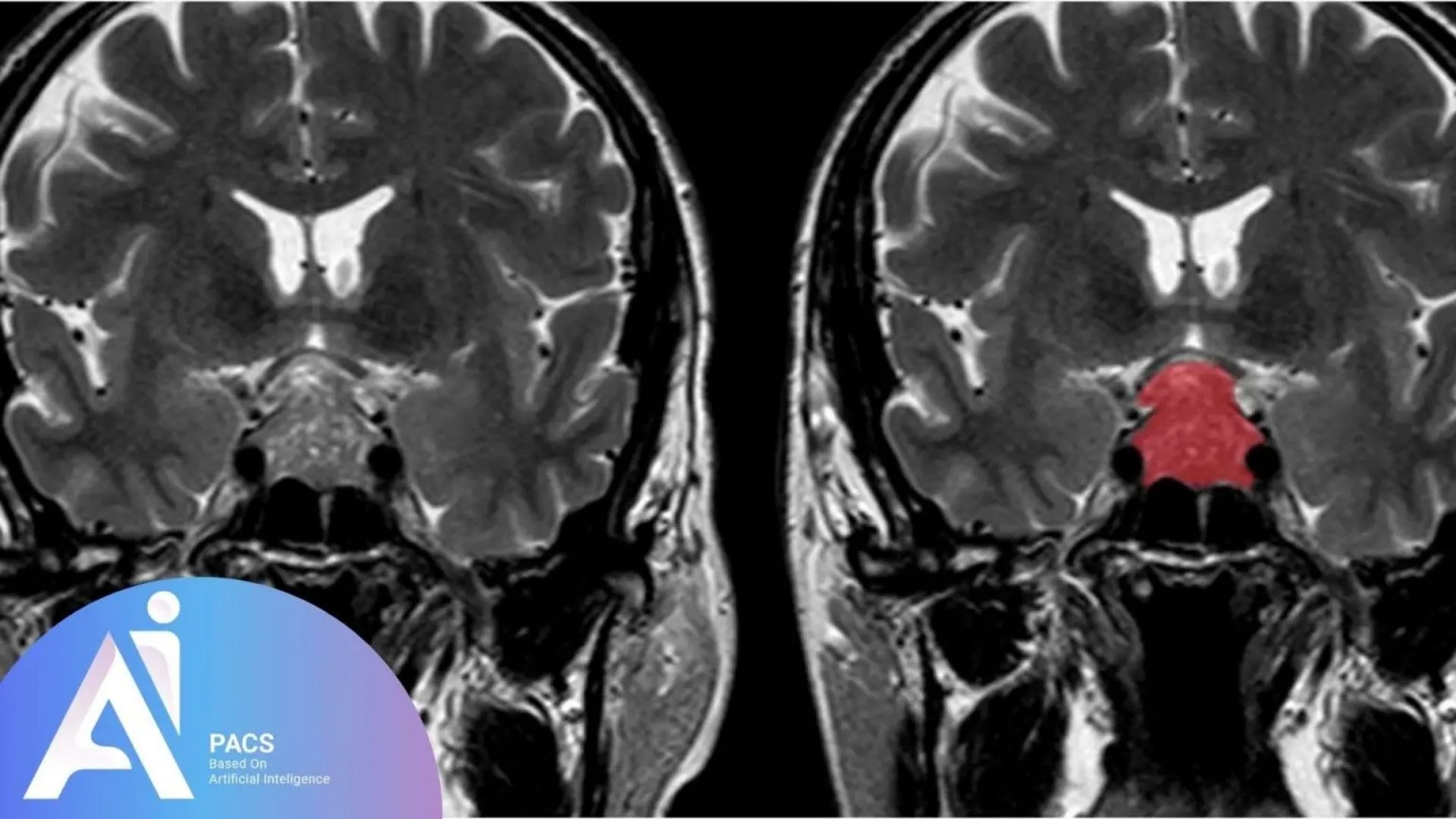
The Role of Dynamic MRI in Pituitary Adenoma Diagnosis
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI is the gold standard for evaluating pituitary adenomas. This imaging technique captures the tumor’s enhancement pattern, improving the detection of small microadenomas and distinguishing them from normal pituitary tissue. It is particularly valuable for:
– Detecting small, hormone-secreting adenomas that may not be visible on standard MRI
– Assessing vascular supply to differentiate tumors from cystic or inflammatory lesions
– Planning for minimally invasive surgery, ensuring precise tumor localization
Treatment Options After Diagnosis
Once diagnosed, the treatment plan for pituitary adenomas is tailored based on the tumor type, size, and the patient’s symptoms. Treatment options include:
- Medications: For tumors like prolactinomas, medications that regulate hormone levels can be effective.
- Surgical Intervention: Larger tumors or those causing significant symptoms may require surgical removal.
- Radiotherapy: In certain cases, radiation therapy is used to shrink the tumor.
Conclusion
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment of pituitary adenomas are essential to prevent complications. MRI, especially dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging, is crucial in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Patients experiencing symptoms or requiring further evaluation should consider consulting with an expert in imaging.
Get your expert radiology report online with the AI-PACS team. Fast, accurate, and hassle-free. Upload your scans now for a professional review!
References:
radiopaedia.org
emedicine
retinatoday





