Applications of MR Defecography
MR defecography is a diagnostic test used in medicine to assess the muscles and organs involved in bowel function. It helps diagnose the causes of bowel disorders and defecation problems such as constipation, incontinence, and other related conditions. This test utilizes X-ray fluoroscopy or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to provide valuable insights into the contraction and relaxation of pelvic floor muscles, the function of the rectum during defecation, the movement of the colon, rectum, vagina, and bladder, as well as conditions such as uterine or bladder prolapse. These insights are highly beneficial for the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions.
If you’re seeking reliable online radiology report services, AI-PACS is here to provide you with the best second opinion on your medical images, delivered by our team of expert radiologists.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Bowel Dysfunction
This test assesses the function of the rectum and pelvic floor muscles in cases such as rectocele, cystocele, enterocele, gastric motility disorders, and other functional bowel defects.
Post-Surgical Complications Assessment
MR defecography is useful after surgeries involving the rectum, such as rectal prolapse repair or abdominal surgeries, to evaluate complications like bowel dysfunction.
Assessment of Defecation Difficulties
It can help determine the cause and precise location of issues such as bowel adhesions.
Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness
MRI defecography test is also used to evaluate the effectiveness of different treatments and their impact on bowel function.
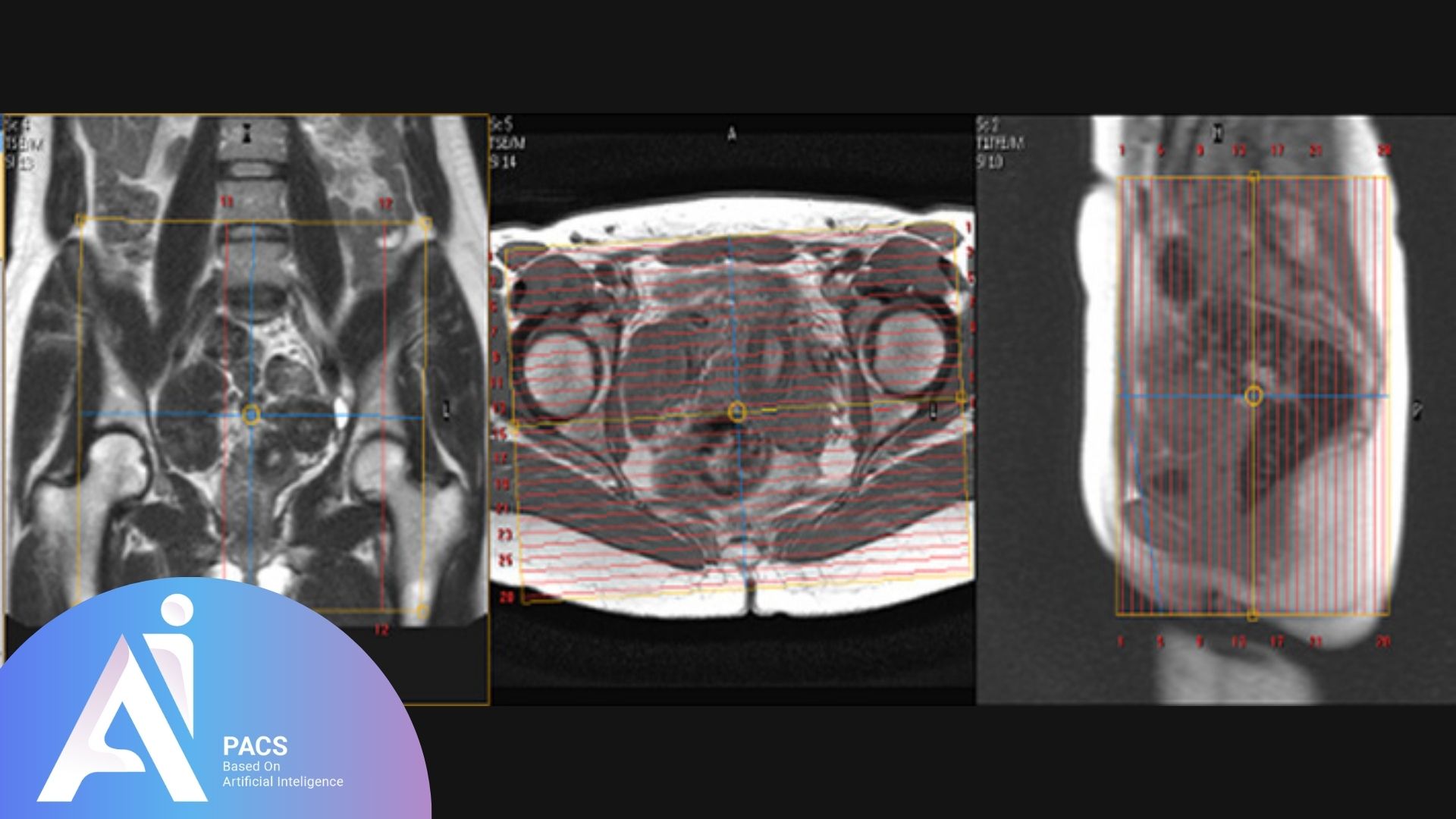
How is MR Defecography Performed?
MRI-Based Defecatory Function Assessment is an important imaging technique for diagnosing conditions like pelvic organ prolapse. Due to the anatomical location and the nature of the condition, patients may hesitate to seek medical evaluation. Therefore, this section explains the procedure in detail.
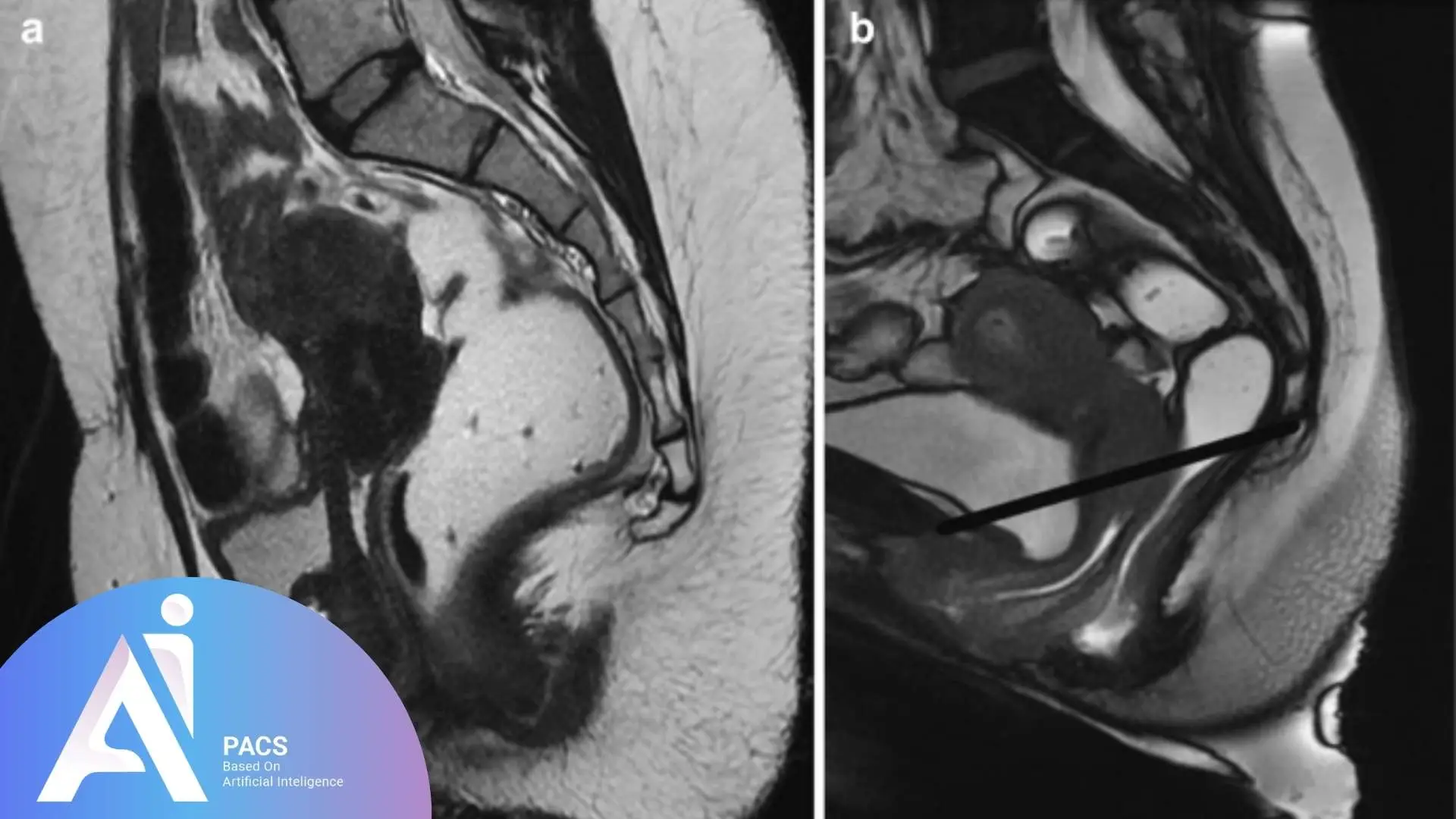
During the test, a rectal gel is injected into the patient’s rectum, and images are taken while the patient expels the gel. This allows the examination of the internal pelvic structures to determine whether the muscles change shape or position under strain, whether there is any muscle damage, the extent of prolapse, and how a surgeon should approach treatment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of MR Defecography
Advantages
- Non-invasive Nature: This test does not require the insertion of instruments or catheters into the body, making it more comfortable for the patient with a lower risk of infection or complications.
- High-Resolution Imaging: MR defecography provides high-quality, detailed images of the bowel and related muscles, allowing for more precise diagnosis of abnormalities, dysfunctions, and structural changes.
- Improved Treatment Planning: The test aids physicians in prescribing more effective treatments for functional bowel disorders.
Disadvantages
- Higher Cost: Compared to other diagnostic tests, MR defecography can be more expensive.
- Longer Analysis Time: This test requires more time to analyze and interpret the data than some other imaging methods.
- Physical Limitations for Some Patients: Certain patients may have physical or mobility restrictions that make the test difficult to perform.

Possible Side Effects of MR Defecography
Since MR defecography test is performed using MRI, no significant side effects have been reported. However, like other imaging tests, there may be some rare complications, including:
Fatigue and Muscle Weakness: Patients may experience mild fatigue or weakness in the lower body after the test, especially those with existing muscular disorders. However, in healthy individuals, this is uncommon.
- Rectal Discomfort: The test may cause mild rectal irritation or discomfort during the procedure.
- Allergic Reactions to Contrast Agents: If a contrast agent is used for imaging, some individuals may have allergic reactions to it.
- Infection Risk: Although extremely rare, there is a minimal risk of infection if hygiene protocols are not strictly followed.
Preparation for MR Defecography
Before undergoing MRI defecography imaging test, certain preparations are required. Here are some key points to consider:
- If you have any medical conditions or are taking specific medications, inform your doctor beforehand.
- Your doctor may ask you to follow a special diet, such as increasing fluid intake or avoiding foods that cause excessive gas.
- Avoid wearing makeup or jewelry during the test, and wear disposable medical clothing provided by the facility.
- Be prepared to remain in a fixed position for approximately 30 to 60 minutes during the procedure.
- Discuss any concerns or the steps involved in the test with your doctor in advance.
Interpretation of MR Defecography Results
MR defecography results must be interpreted by a specialist. In general, the physician analyzes the obtained images to assess bowel and muscle function. The test can help diagnose conditions such as:
- Rectocele: A condition where part of the posterior vaginal wall bulges forward, pushing the rectum into the vagina. The test determines its severity and extent.
- Cystocele: A condition where the bladder bulges into the vaginal wall, causing incomplete bladder emptying and frequent urination. The test evaluates its severity and impact on bowel function.
- Colonic Dysmotility: A condition where the colon muscles do not function properly, leading to reduced bowel movement and symptoms like indigestion and bloating. MR defecography helps diagnose issues such as abnormal gastric motility or bowel adhesions.
- Post-Surgical Complications: If a patient has undergone bowel-related surgery, MR defecography helps evaluate post-surgical complications and the effectiveness of the procedure.
Treatment Options After Diagnosis
Once abnormalities are detected through MR defecography, various treatment options may be recommended based on the severity and type of dysfunction. These include:
- Pelvic Floor Therapy: Specialized exercises and biofeedback techniques to strengthen the pelvic muscles and improve bowel function.
- Medications: Laxatives, stool softeners, or medications that regulate bowel motility may be prescribed.
- Dietary Adjustments: Increasing fiber intake, staying hydrated, and consuming probiotics can help manage conditions like constipation and dysmotility.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: In cases of severe prolapse or obstruction, non-surgical interventions like injections or electrical stimulation may be suggested.
- Surgical Interventions: If conservative treatments fail, surgical options such as rectopexy, colonic resection, or pelvic floor reconstruction may be necessary.
The H Line in Defecography
The H Line in defecography represents a reference line between different regions of the bowel, indicating changes in bowel movement patterns. Analyzing the H Line helps physicians diagnose conditions such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), IBS with diarrhea (IBS-D), or IBS with constipation (IBS-C).
Comparison of MRI Defecography with Other Diagnostic Methods
Here, we compare MR defecography with other diagnostic imaging techniques such as CT scans and ultrasound:
- MRI does not use ionizing X-rays, making it safer compared to imaging techniques like CT scans.
- MRI is more specialized than radiology, ultrasound, and CT scans, which provide more general assessments.
- MRI provides higher-resolution images of pelvic floor muscles and soft tissues, offering more precise diagnostic information.
Final Thoughts
MR defecography is a crucial diagnostic tool for evaluating bowel and pelvic floor dysfunctions. By providing high-resolution imaging, it allows physicians to diagnose and tailor treatment strategies effectively. While it has some limitations, such as cost and time requirements, its non-invasive nature and diagnostic accuracy make it an essential option for patients with defecation disorders. As medical technology advances, MRI defecography will continue to play a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
References:
Radiologyinfo
Clevelandclinic
Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine