Understanding Your Prostate MRI Report
Prostate MRI is a medical imaging technique used to evaluate and diagnose issues related to the prostate gland. It is particularly effective in identifying conditions such as prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and prostate infections. This method utilizes magnetic waves and radiofrequency pulses to create detailed images of the prostate and surrounding tissues, without the need for X-rays or surgery.
How Is Prostate MRI Performed?
In the past, prostate MRI involved inserting a device into the rectum to enhance diagnostic accuracy due to its proximity to the prostate. Modern advancements in MRI technology, such as improved imaging resolution and powerful magnetic fields, have eliminated the need for this invasive step.
During the procedure, the patient lies down on a specialized table that slides into the MRI machine. The device uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create cross-sectional and 3D images of the prostate. In some cases, a contrast agent (gadolinium) may be injected to improve image clarity and diagnostic precision.
Applications of Prostate MRI
Early Detection of Prostate Cancer: One of the most critical uses of prostate MRI is the precise and early detection of prostate cancer. This technique can identify suspicious areas with high accuracy.
Assessing Disease Progression: Prostate MRI helps determine whether prostate cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, bones, or nearby organs. If your doctor suspects that prostate cancer has spread, upload your imaging to AI-PACS for a detailed review so you can understand the next steps with confidence.
Treatment Planning: Based on MRI results, doctors can create tailored treatment plans, including surgery, radiation therapy, or active surveillance.
Evaluating Treatment Outcomes: Prostate MRI is also used to monitor and assess the effectiveness of treatments such as radiotherapy or surgery.
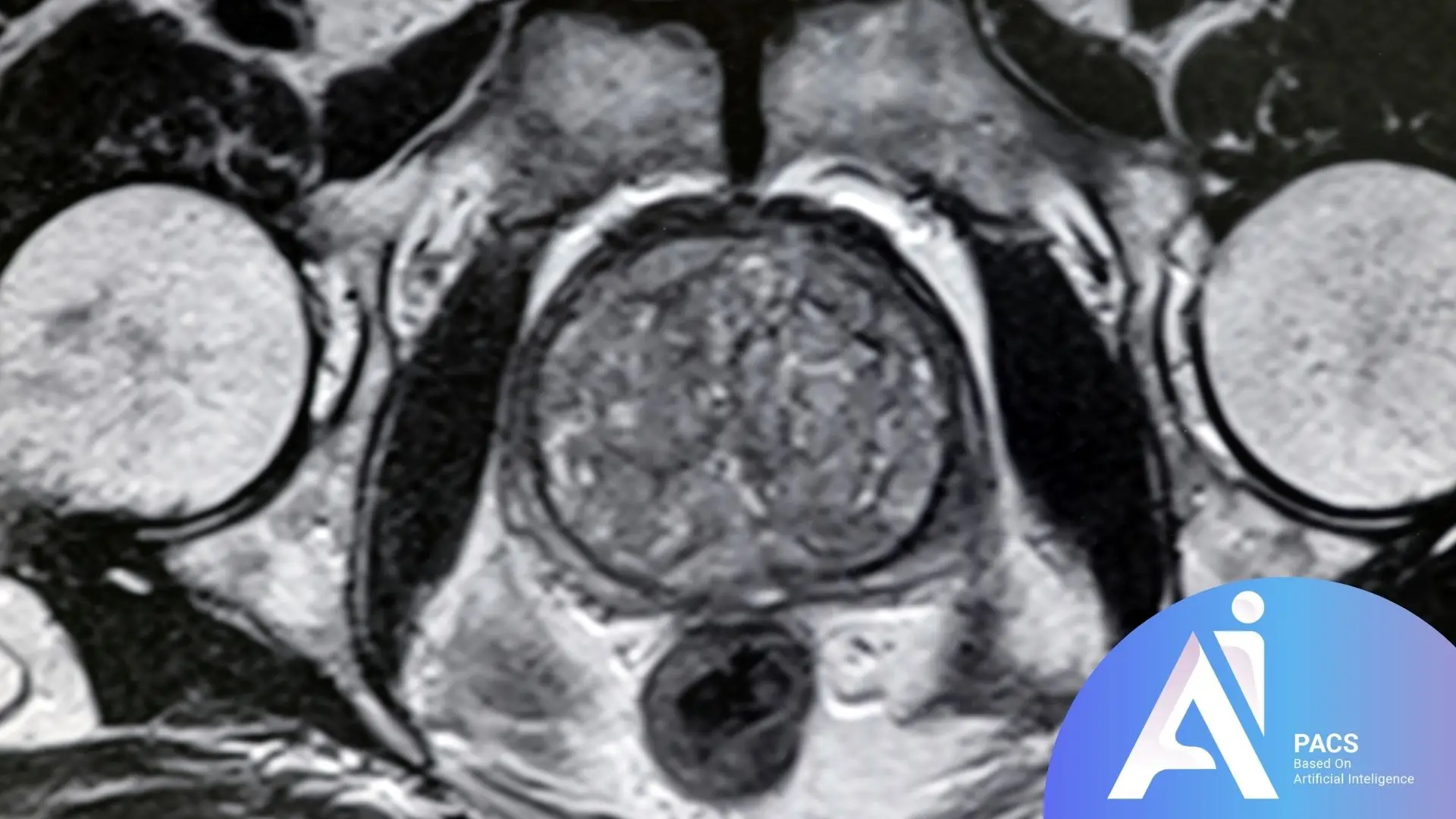
Key Terms in Prostate MRI Reports
Prostate MRI reports include specialized terminology to describe findings and assess the condition of the prostate. Understanding these terms is crucial for specialists to make accurate diagnoses and for patients to be informed participants in their healthcare decisions. Below are some commonly used terms:
Peripheral Zone (PZ)
The area of the prostate where most prostate cancers develop. It appears as a high-signal region on T2-weighted images.
Transition Zone (TZ)
Often associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Abnormal signal changes in this zone may indicate prostate cancer.
Central Zone (CZ)
Located near the prostate base and the urethral entry, this area is less commonly affected by cancer compared to the peripheral zone.
Adenomatous
Refers to benign changes in the transitional zone, often caused by BPH.
Hemorrhage
Indicates the presence of bleeding within the prostate, often due to a biopsy or other conditions. It appears as high-signal areas on T1-weighted images.
Low/High Signal Intensity
Refers to the brightness or darkness of specific areas in MRI images. Low signals may indicate cancerous or fibrotic tissue, while high signals often represent normal or benign structures.
PI-RADS (Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System)
A scoring system used to grade suspicious areas in the prostate based on mpMRI results. Scores range from 1 to 5:
- PI-RADS 1: Very low likelihood of cancer
- PI-RADS 2: Low likelihood of cancer
- PI-RADS 3: Intermediate likelihood of cancer
- PI-RADS 4: High likelihood of cancer
- PI-RADS 5: Very high likelihood of cancer
Capsular Invasion
Refers to cancer extending beyond the prostate gland into the prostate capsule, often indicating advanced disease.
Capsular Thickening
Increased thickness of the prostate capsule, which may be caused by inflammation, fibrosis, or cancer.
Perineural Infiltration
The presence of cancer cells around the nerves of the prostate, suggesting localized tumor spread.
Perineural Spread
Describes cancer spreading along the nerve pathways within the prostate, often associated with advanced stages.
Mass Effect
A mass within the prostate that exerts pressure on nearby structures, causing deformation or displacement.
Heterogeneity
Non-uniform signal changes in the prostate, which may indicate abnormal masses, fibrotic areas, or necrotic regions.
Seminal Vesicle Invasion
Occurs when prostate cancer spreads to the seminal vesicles located near the prostate.
Extraprostatic Extension (EPE)
Refers to the spread of prostate cancer beyond the prostate capsule, indicating disease progression beyond the gland.
Final Thoughts
Interpreting prostate MRI is a complex and specialized process that requires in-depth knowledge of prostate anatomy and pathology. By using high-resolution imaging and the PI-RADS scoring system, prostate MRI facilitates accurate diagnosis and better management of prostate conditions, particularly cancer. Proper interpretation of these scans can lead to effective treatment planning and improved patient outcomes. MRI results help guide critical decisions, such as whether active surveillance, surgery, or radiation therapy is the most appropriate approach for the patient’s specific condition. Ultimately, prostate MRI is a valuable tool for early detection and monitoring of prostate diseases.
References:



