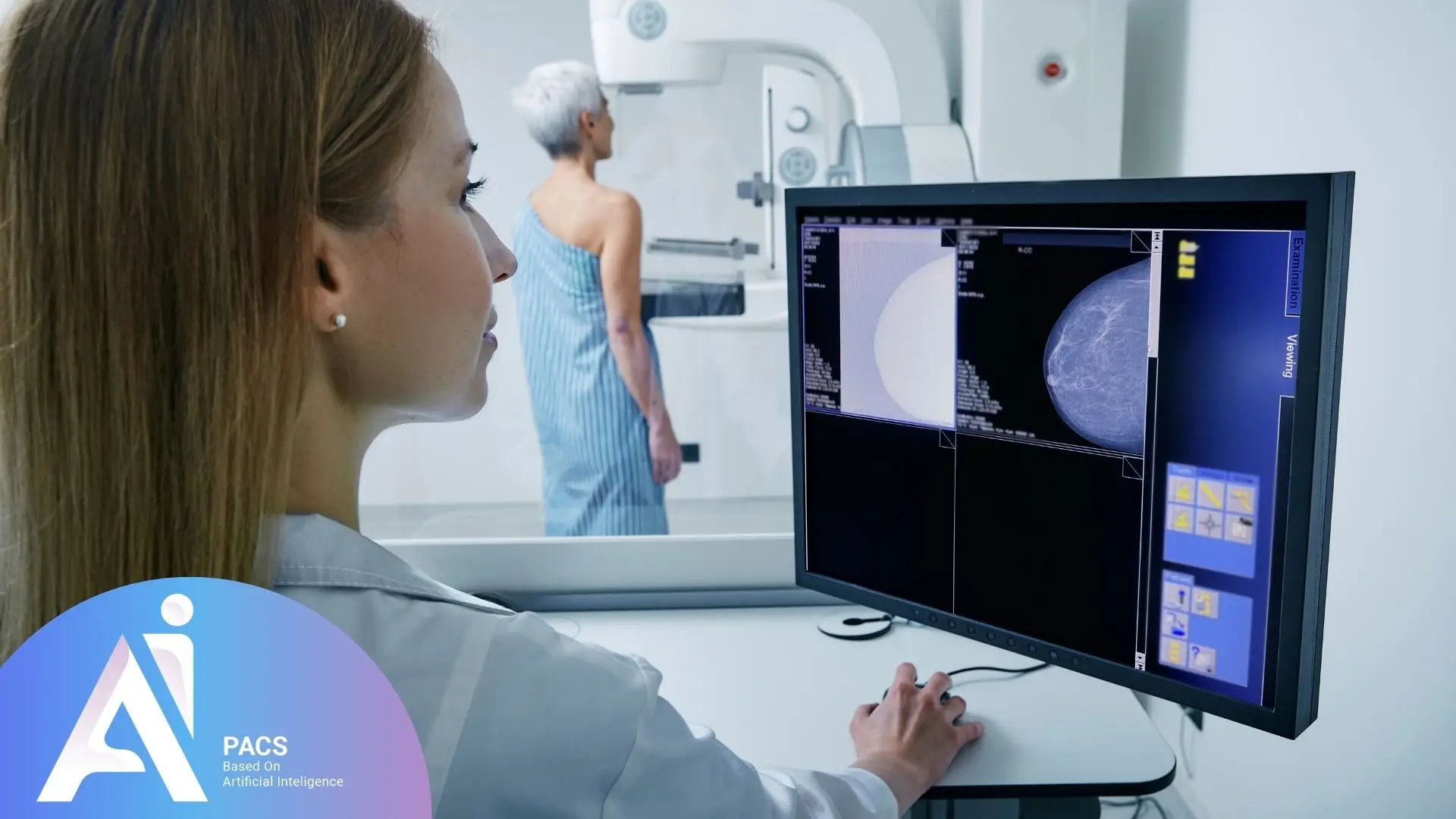
The Importance of Mammography Results
Mammography is a vital tool for the early detection of breast cancer. Studies show that it can reduce mortality rates by up to 40%, making it an essential method for identifying breast abnormalities before they become life-threatening. The significance of mammography results is notable for several reasons:
Early Detection of Breast Cancer: Mammography can identify small changes and cancerous masses in the breast that are not detectable through physical examination. Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes and prognosis.
Reduced Mortality:
Identifying Breast Changes: Mammography can detect non-cancerous changes such as cysts and fibroadenomas, helping doctors select the most appropriate treatment. Not sure if your mammography results show harmless changes or something serious? Submit your report to AI-PACS and let our specialists explain your results in simple terms.
Treatment Monitoring: For patients with a history of breast cancer, mammography is used to monitor treatment outcomes and ensure the disease has not returned.
Surgical Planning: Mammography results assist physicians in choosing the appropriate surgical approach for cancer patients, such as lumpectomy or mastectomy.
Specialized Terminology in Mammography
Understanding specialized terms in mammography is crucial for interpreting its results. For instance, knowing the meaning of ‘breast density’ can help patients understand why additional imaging might be required, while terms like ‘BI-RADS categories’ guide physicians in determining whether a biopsy is necessary, ultimately aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Here are some common terms:
Terms Related to Images and Results
- Mammogram: An X-ray image of the breast taken during a mammography procedure.
- Breast Density: The proportion of glandular tissue to fatty tissue in the breast. Dense breasts may require more thorough evaluations.
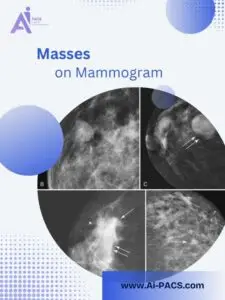
- Mass: Any abnormal structure in the breast, which could be solid (like a tumor) or cystic (fluid-filled).
- Calcification: Small calcium deposits in breast tissue that appear as bright spots on a mammogram. These can be benign or indicative of cancer.
BI-RADS System
The Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) categorizes mammography findings to assess the risk of breast cancer. Categories range from 0 to 6:
- BI-RADS 0: Incomplete – additional evaluation needed.
- BI-RADS 1: Normal – no findings.
- BI-RADS 2: Benign findings.
- BI-RADS 3: Probably benign – requires short-term follow-up.
- BI-RADS 4: Suspicious abnormality – biopsy recommended.
- BI-RADS 5: Highly suspicious – biopsy strongly indicated.
- BI-RADS 6: Confirmed malignancy.
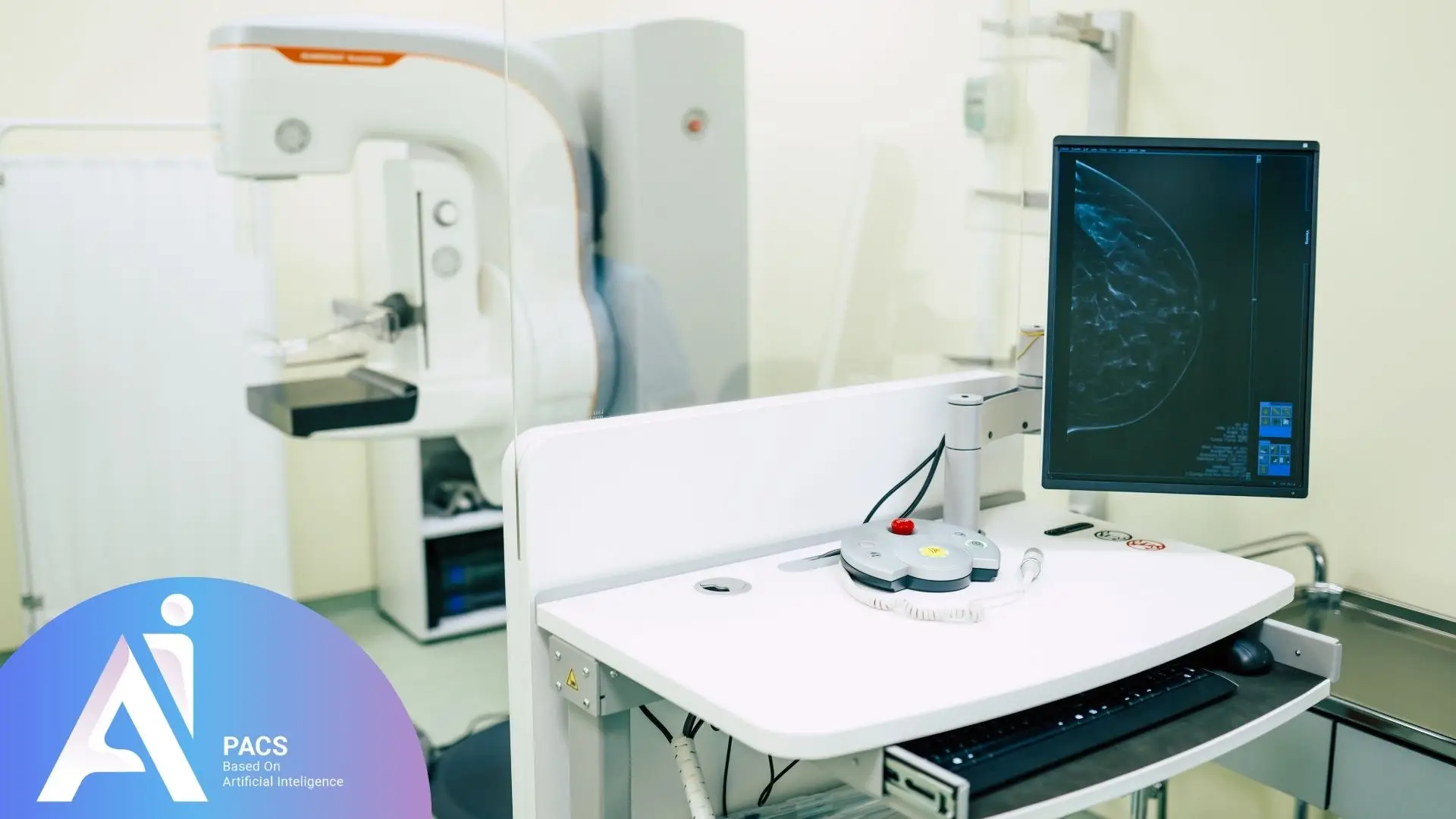
What Are Mammography Results?
Mammography results typically include radiographic images of breast tissue reviewed by a radiologist. After interpretation, the radiologist provides a detailed report that highlights any abnormalities, along with recommendations for follow-up actions or additional imaging if needed. This report is then shared with the patient’s physician, who discusses the findings and next steps with the patient.
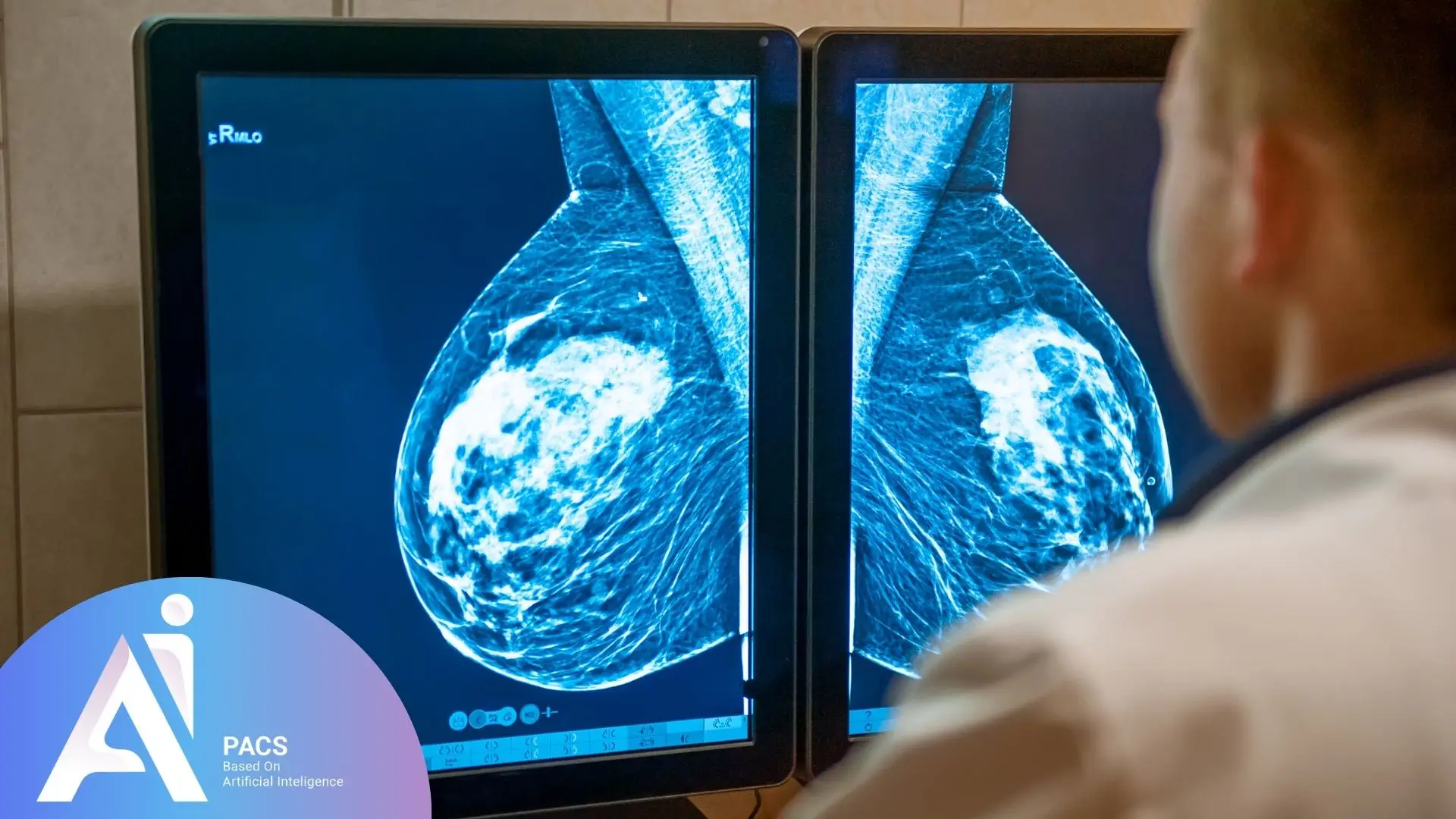
Interpreting Mammography Results
Radiologists focus on specific indicators when interpreting mammography images:
- Masses and Nodules: These may be solid or cystic. Solid masses often require further examination.
- Microcalcifications: These tiny spots may indicate cellular changes and often necessitate a biopsy.
- Symmetry and Tissue Structure: Radiologists check for asymmetry or changes in the normal structure of breast tissue.
Recommendations for Mammography
- Women aged 40 and above are advised to undergo annual mammography screenings.
- For those with risk factors, such as a family history of breast cancer, consulting a physician for more frequent or earlier screenings is recommended.
Conclusion
Mammography is a cornerstone for the early detection of breast cancer, transitioning ambiguity into clarity and peace of mind. Although mammography images may initially appear complex, expert interpretation by specialists transforms these images into actionable insights, guiding necessary medical decisions. These interpretations often guide critical treatment decisions, such as determining the need for further imaging, recommending biopsies, or reassuring patients when results are normal. By providing clear next steps, they help patients move forward with confidence, whether that involves starting treatment or maintaining routine screenings. Understanding and correctly interpreting results empower women to seek timely treatment or gain reassurance about their health. Mammography interpretation bridges the gap between concern and informed decision-making for a healthier future. If you are looking to understand your mammogram results better, click here to learn more about mammography calcification and what it means.
References: