What Your Abdominal and Pelvic CT Scan Can Tell Us
These scans provide incredibly detailed cross-sectional images of your internal organs, blood vessels, and soft tissues. When I review your scan, I’m looking for any changes from normal anatomy that might explain your symptoms or health concerns. The beauty of CT imaging is its ability to detect issues early, often before they become serious problems.
A detailed radiology report doesn’t just identify potential issues like tumors, infections, or structural irregularities – it also guides your doctor in developing the most effective treatment plan. Understanding these findings ensures you receive timely medical care, which can significantly improve your outcomes.
Preparing for Your CT Scan
What You Need to Know
Before your scan, there are several important steps to ensure we get the clearest possible images:
Fasting Requirements: You’ll typically need to avoid eating for 4-6 hours before your scan. This helps us see your organs more clearly and reduces the risk of nausea if contrast dye is used.
Contrast Agent Information: Many abdominal CT scans require contrast dye, which we give either by mouth (oral contrast) or through an IV (intravenous contrast). This special dye helps highlight your organs and blood vessels, making abnormalities easier to spot. Don’t worry – most patients tolerate contrast well, though some experience a brief warm sensation. Pre-scan preparation and blood work may be required.
During the Scan: You’ll lie on a table that slides through a large, donut-shaped machine. The actual scanning takes just a few minutes, but you’ll need to hold your breath for 10-15 seconds at a time to prevent blurring. I always tell my patients it’s like holding your breath in a swimming pool – completely manageable.
Radiation Safety: CT scans do use X-rays, but the amount of radiation is carefully controlled and considered safe for diagnostic purposes. The benefits of accurate diagnosis far outweigh the minimal radiation risk. To put it in perspective, the radiation from an abdominal CT scan is roughly equivalent to what you’d naturally receive over 2-3 years from background sources.
If you want to learn more about what to expect before your appointment, read CT Scan Preparation: Everything You Need to Know Before Your Appointment. It provides step-by-step guidance on fasting, contrast agents, and safety considerations.
Common Conditions Detected by Abdominal Pelvic Imaging
CT scans play a crucial role in modern medicine, helping us detect and diagnose a variety of conditions with remarkable precision. Here are the most common findings I encounter:
Inflammatory Conditions
- Appendicitis: Often my first concern in patients with right lower abdominal pain. CT scan is a powerful tool for diagnosing appendicitis and other abdominal emergencies.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas that can cause severe pain
- Inflammatory bowel disease: Including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
- Diverticulitis: Infection of small pouches in the intestinal wall
Infections and Abscesses
- Deep-seated infections: Hidden pockets of infection that might not be obvious clinically
- Abscesses: Collections of infected fluid that often require drainage
Deep-seated infections or abscesses require immediate intervention.
Tumors and Masses
Here’s something that often surprises patients: finding a “mass” doesn’t automatically mean cancer. In my experience, many masses turn out to be benign cysts, scar tissue, or other non-cancerous conditions. However, CT scans are excellent at:
- Locating tumors: Both benign and malignant growths
- Staging cancer: Determining how far cancer has spread
- Monitoring treatment response: Tracking how tumors respond to therapy
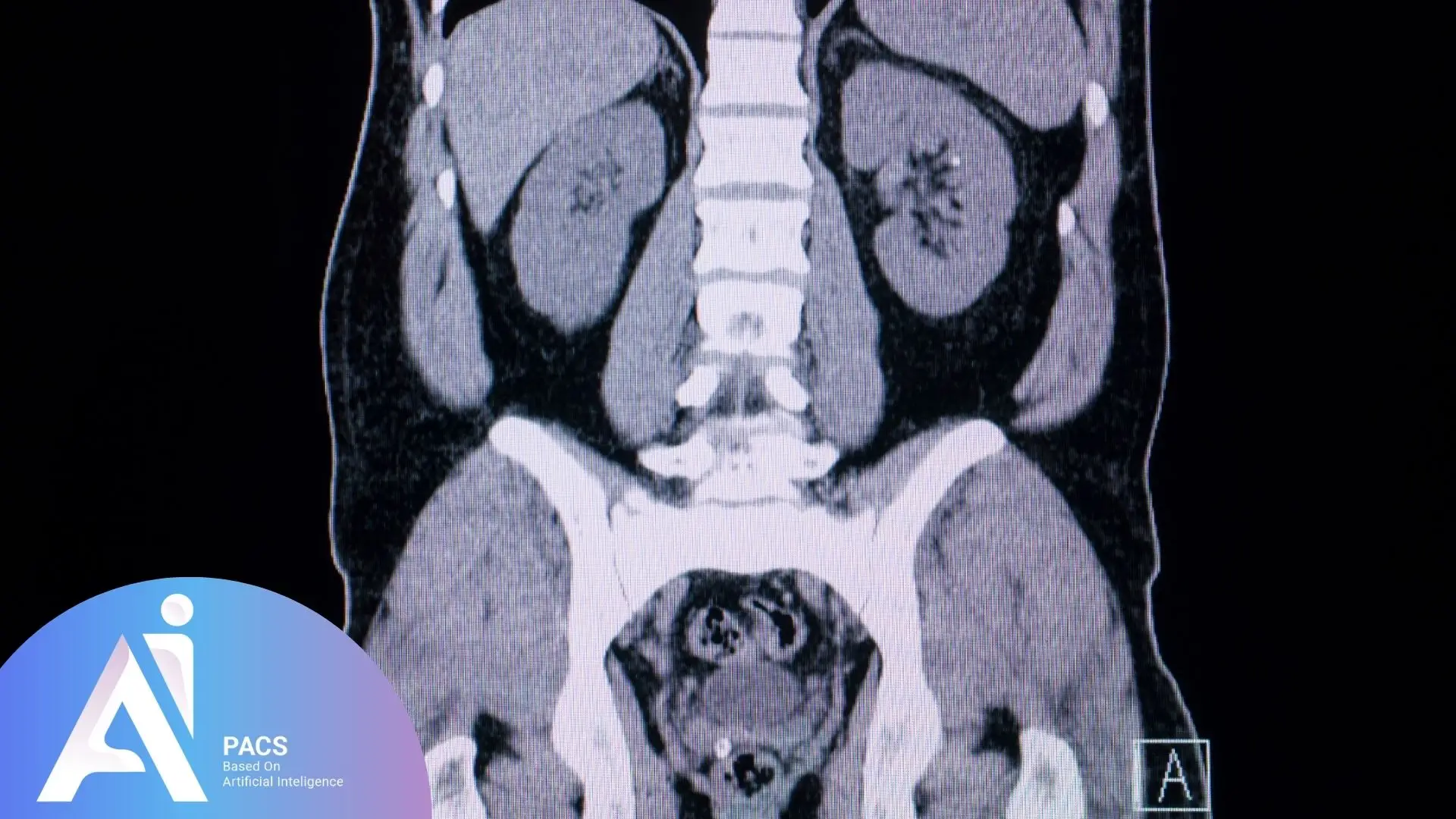
Kidney and Bladder Issues
- Kidney stones: CT scans can spot even tiny stones that might cause future problems
- Bladder stones: Less common but easily detected
- Kidney infections: Including serious complications like abscesses
Trauma-Related Injuries
In emergency situations, CT scans are invaluable for detecting:
- Internal bleeding: Even small amounts that might not be obvious
- Organ damage: Tears or bruising to internal organs
- Fractures: Particularly in the pelvis or spine
Each of these conditions requires specialized expertise for accurate interpretation. Expert abdominal imaging consultation ensures that subtle findings are not overlooked and that you receive appropriate guidance for follow-up care.
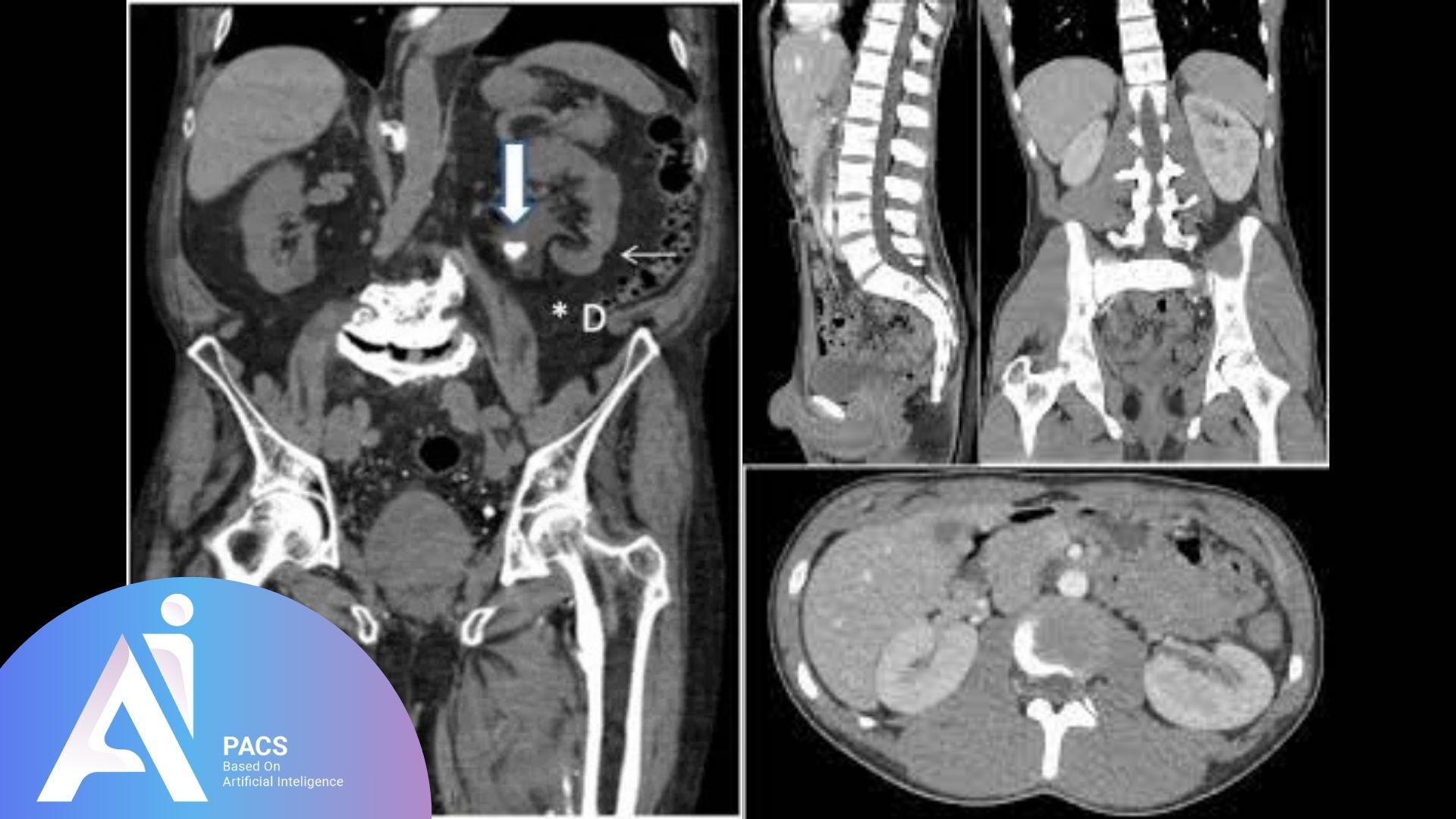
How to Understand Your Abdominal and Pelvic CT Scan Report
Key Terms Explained
When you receive your CT report, you might encounter medical terms that seem confusing. Here’s what they mean in plain English:
Mass or Lesion: These words often worry patients, but they simply mean “something that looks different from normal tissue.” Many masses are benign (non-cancerous) cysts or scar tissue. I always tell my patients that finding something doesn’t automatically mean it’s serious – it just means we need to investigate further.
Enhancement: This refers to how a structure appears after we give you contrast dye. Some areas “light up” more than others, which helps us distinguish between different types of tissue. It’s like using a highlighter to make certain parts of a document stand out.
Cyst: A fluid-filled sac that’s usually harmless. I see these on scans daily – they’re incredibly common and rarely cause problems.
Calcification: Calcium deposits in soft tissues. While sometimes linked to disease, calcifications are often just signs of normal aging or old, healed injuries.
Effusion: Excess fluid buildup in body cavities. This can indicate inflammation, infection, or other conditions that need attention.
Hypodense/Hyperdense: These terms describe how dark or light an area appears on the scan. Hypodense areas appear darker and usually contain less dense tissue (like fat or fluid). Hyperdense areas appear lighter and contain denser tissue (like bone or some types of tumors).
Lymphadenopathy: Enlarged lymph nodes, which can indicate your body is fighting an infection or, less commonly, may suggest cancer spread.
Aneurysm: An abnormal bulging of a blood vessel that requires careful monitoring or treatment.
Stenosis: Narrowing of a duct or blood vessel that might affect normal function.
Specific Organ Findings
Hepatomegaly: An enlarged liver, often due to fatty liver disease, infection, or other conditions.
Splenomegaly: An enlarged spleen, which may indicate infection, blood disorders, or other conditions.
Cholelithiasis: The medical term for gallstones, which I see frequently and can often be managed without surgery.
Nephrolithiasis: Kidney stones, ranging from tiny crystals to large stones that require treatment.
Hydronephrosis: Swelling of the kidney due to blocked urine flow, which needs prompt attention. If your kidney function is borderline, particularly for kidney stone evaluation.
What Happens After Your CT Scan: Next Steps
Once your scan is completed, the next crucial step is expert radiologist consultation to interpret your results. As a radiologist, I carefully examine every image, looking for signs of inflammation, infections, abnormal growths, or structural issues.
Based on my findings, your doctor may recommend various treatment options such as medication, dietary adjustments, or follow-up imaging. Sometimes, we need additional studies like MRI or ultrasound to get more detailed information about specific findings.
The urgency of follow-up care depends entirely on what we find. Some findings require immediate attention, while others can be monitored over time. This is why having an experienced radiologist review your scan is so important – we can distinguish between urgent findings and those that can wait.
When Expert Interpretation Makes a Difference
Throughout my career, I’ve seen how professional CT scan analysis can make a significant difference in patient outcomes. Sometimes, subtle findings that might be overlooked can be the key to early diagnosis and treatment.
If you’re concerned about your results or want additional peace of mind, consider seeking a second opinion. Many patients find that having another radiologist review their scan provides valuable reassurance or catches important details that might have been missed.
For those wanting to better understand their reports, I recommend learning about how to read your complete CT scan report, which can help you navigate the medical terminology and understand what your results mean.
Final Thoughts
A CT scan provides invaluable insights into your health, but expert interpretation is essential for accurate diagnosis. While understanding basic terminology and findings can help you grasp your condition, medical consultation remains crucial for proper treatment planning.
I’ve found that patients who understand their CT results are more engaged in their care and better able to make informed decisions about treatment options. However, it’s important to remember that CT scan reports should always be reviewed alongside your medical history and symptoms – we use this combined information to form the most accurate diagnosis possible.
If you’re feeling uncertain about your results or want additional expert review, don’t hesitate to get a second opinion on your CT scan. Timely follow-ups and appropriate treatments based on CT findings can lead to better health outcomes, and having confidence in your diagnosis is an important part of that process.
Remember, as your radiologist, I’m here to help you understand your health through the lens of medical imaging. Every scan tells a story, and my job is to help you and your doctor understand that story clearly and completely.
Abdominal and pelvic CT interpretation encompasses numerous organ systems and potential pathologies. Given the complexity of these scans and the variety of conditions they can detect, professional radiological review ensures you receive comprehensive understanding of your results and appropriate guidance for your healthcare decisions.
References: