Does MRI Show Blood Clots?
Does MRI show blood clots is a question many people ask during moments of fear or uncertainty, often after sudden pain, swelling, headaches, or neurological symptoms, and understanding the correct answer can bring reassurance, clarity, and safer medical decisions. Blood clots can be serious, and choosing the right imaging test is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. While MRI is capable of detecting certain types of blood clots, it is not always the first or best option. The effectiveness of MRI depends on the location of the clot, the urgency of symptoms, and the patient’s overall condition.
What Blood Clots Are and Why Imaging Matters
A blood clot forms when blood thickens and sticks together inside a vein or artery, slowing or blocking normal circulation. Some clots remain harmless, but others can travel or grow, cutting off blood supply to vital organs such as the brain or lungs.
Because symptoms can be vague, imaging is often necessary to confirm a diagnosis. Leg pain, swelling, chest discomfort, or headaches can have many causes, and imaging allows doctors to see what is actually happening inside the body. Accurate imaging helps confirm the presence of a clot, identify its location, determine its age, and guide appropriate treatment.
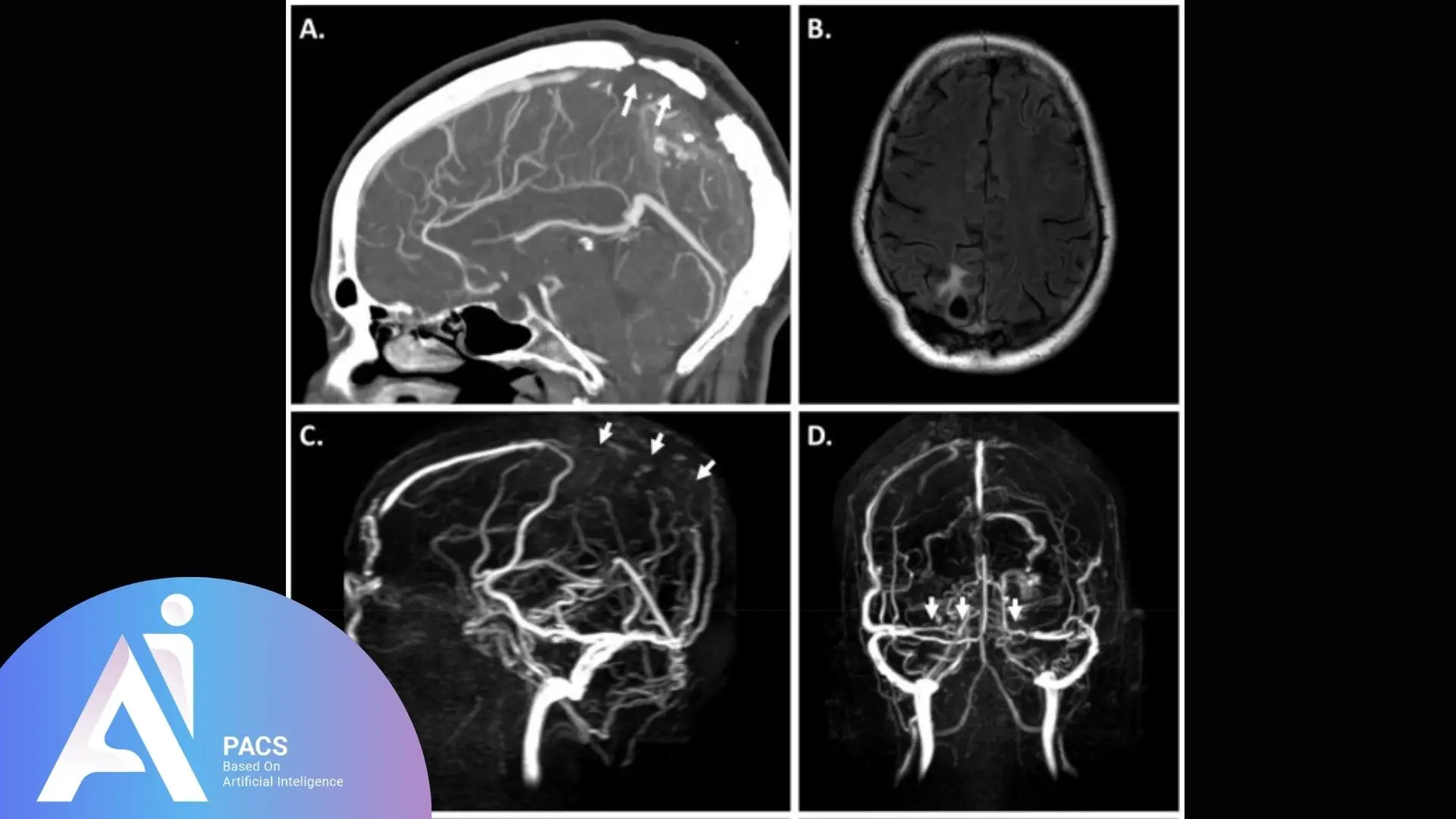
Does MRI Show Blood Clots in the Brain?
MRI is one of the most powerful imaging tools for detecting blood clots in the brain. It is commonly used when patients experience unexplained headaches, weakness, vision changes, seizures, or speech difficulties.
MRI can detect clots related to ischemic stroke, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, and other disorders affecting blood flow in the brain. Specialized techniques such as MR angiography and MR venography allow detailed visualization of arteries and veins, often identifying clots even at an early stage.
Clinical symptoms and imaging must always be considered together, as some changes seen on MRI may reflect old or chronic conditions rather than a new clot.
Does MRI Show Blood Clots in the Legs?
Many people asking does MRI show blood clots are concerned about deep vein thrombosis in the legs. Although MRI can detect leg clots, it is usually not the first imaging test performed.
Ultrasound is often preferred because it is fast, widely available, and highly effective for identifying clots in the thigh and calf veins. MRI may be used when ultrasound results are inconclusive or when deeper veins in the pelvis are suspected to be involved.
In patients with complex medical histories or prior clots, MRI can provide additional detail that supports accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Can MRI Detect Blood Clots in the Lungs?
MRI is not typically used to diagnose blood clots in the lungs, known as pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism can be life threatening and requires fast diagnosis, which is why CT pulmonary angiography is usually the first choice.
CT scans provide rapid, clear images of the pulmonary arteries, allowing doctors to confirm or rule out a clot quickly. MRI may be considered in rare circumstances, such as when a patient cannot receive CT contrast or in selected follow up cases.
How MRI Detects Blood Clots
MRI does not directly photograph a clot. Instead, it identifies changes in blood flow and tissue signal characteristics within blood vessels.
A clot may appear as abnormal signal intensity, absence of normal blood movement, or enhancement patterns after contrast administration. In some situations, MRI can help distinguish between an acute clot and an older, organized clot, which can influence treatment decisions.
The accuracy of MRI depends not only on the technology used but also on the expertise of the radiologist interpreting the images.
MRI vs CT vs Ultrasound for Blood Clot Detection
Each imaging method has strengths and limitations, and doctors choose based on the suspected clot location and urgency.
MRI is particularly well suited for brain and pelvic venous clots and does not use ionizing radiation. CT is faster and remains the preferred option for lung clots. Ultrasound is usually the first choice for leg clots because it is accessible, quick, and effective.
Many patients want to better understand why one scan is chosen over another, which is explained in more detail in MRI vs. CT Scan: Key Differences and Best Uses for Diagnosis, helping patients feel more confident about imaging decisions.
When MRI Is Not the Right Choice
Despite its strengths, MRI is not ideal in every situation. Emergency conditions often require faster imaging. Some patients cannot undergo MRI because of implanted medical devices or severe claustrophobia.
In these cases, CT or ultrasound may provide safer and faster answers. The goal is always to choose the test that delivers accurate results with the least risk and delay.
Symptoms That May Prompt Imaging for Blood Clots
Doctors may recommend imaging if a patient presents with unexplained leg swelling, persistent headaches, neurological symptoms, vision changes, shortness of breath, or chest pain. These symptoms do not always mean a clot is present, but imaging helps rule out dangerous causes.
When it comes to headaches or neurological symptoms, understanding when imaging is appropriate can reduce anxiety and prevent unnecessary delays in care.
Why Expert Review Makes a Difference
Imaging results do not interpret themselves. Blood clots can appear differently depending on their age, size, and location, and subtle findings can be missed without careful review.
For patients seeking reassurance or a second opinion, an online MRI reporting service reviewed by Dr. Alizadeh can help clarify whether MRI findings truly suggest the presence of a blood clot and what steps should follow next.
Expert interpretation ensures that imaging findings are placed in the correct clinical context and that patients receive clear answers rather than confusion.
Final Thoughts
Does MRI show blood clots? In many cases, yes, particularly in the brain and deep venous structures, but it is not a universal solution. Choosing the correct imaging test and ensuring skilled interpretation are key to accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Understanding how MRI fits into blood clot detection helps patients ask better questions, reduce uncertainty, and take an active role in their medical care.

