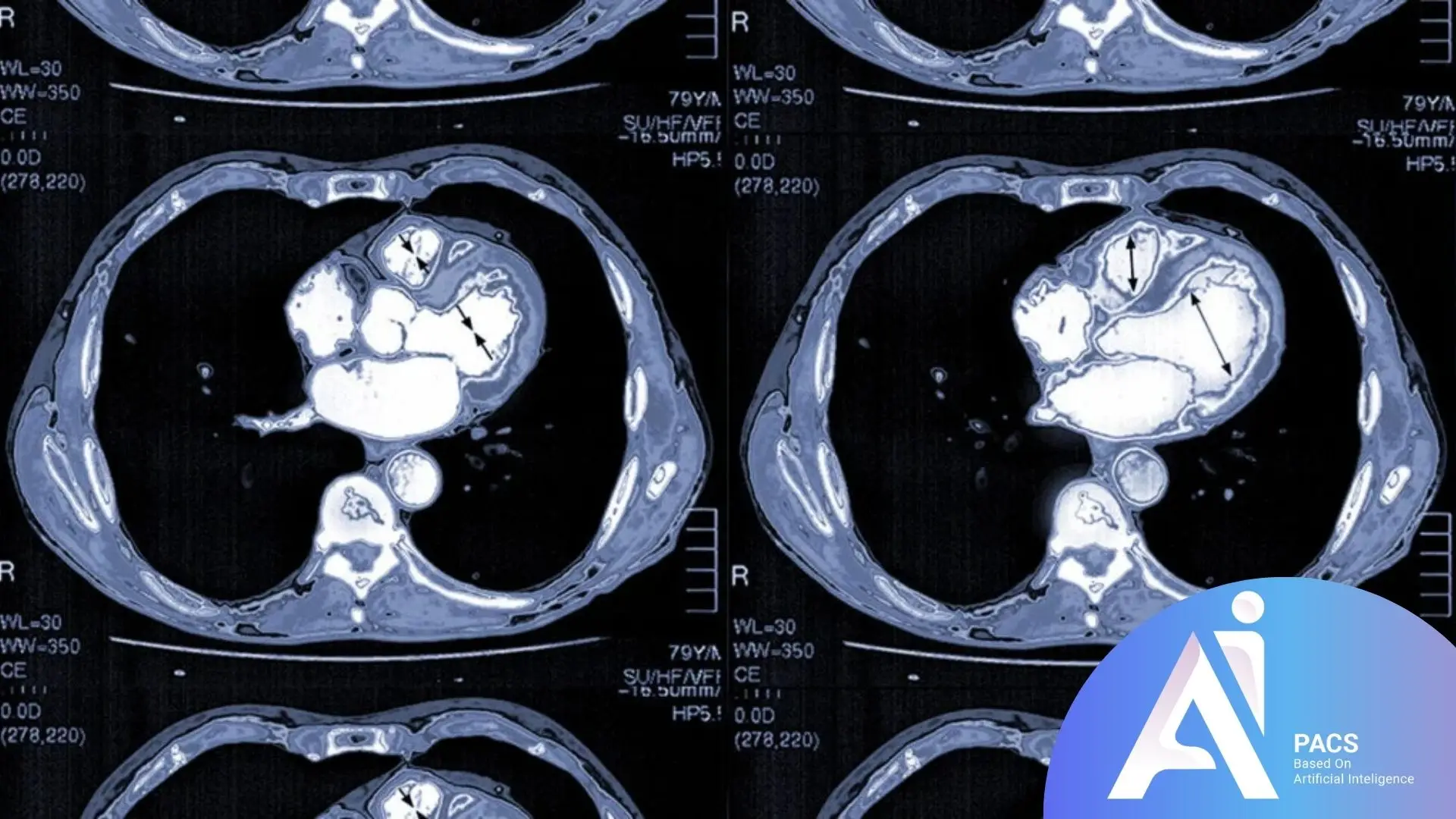
How to Interpret Your Heart CT Scan Result?
A cardiac CT scan is a valuable diagnostic tool that offers numerous benefits for heart health evaluation.
Accurate Diagnosis of Heart Diseases: It helps physicians precisely diagnose various heart conditions, including coronary artery stenosis, arterial blockages, and other structural abnormalities (blood clots in coronary arteries and other vascular conditions).
Assessing Heart Attack Risk: This method can identify calcified and non-calcified plaques in coronary arteries, providing vital information for evaluating heart attack risks.
Non-Invasive and Safe: A cardiac CT scan minimizes the need for invasive procedures like cardiac catheterization, significantly reducing associated risks and complications.
High Speed and Precision: This imaging technique offers swift and highly detailed visualizations, enabling timely and accurate diagnoses without delays.
Treatment Planning: The information obtained from this procedure aids physicians in devising appropriate treatment plans, including decisions about surgical or medical interventions.
Overall, cardiac CT is an indispensable tool for diagnosing and managing heart diseases with high accuracy and minimal invasiveness, contributing to improved patient outcomes.

Common Terms in Cardiac CT Reports
Heart CT Scan Results include specialized terms that provide invaluable insights compared to other imaging methods into the heart and arteries, essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Key terms include:
Calcium Score
Indicates the level of calcium deposits in coronary artery walls, often associated with the risk of coronary artery disease.
Stenosis
Refers to the narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries, which can restrict blood flow to the heart muscle.
Plaque
Deposits of fat, calcium, and other substances within the walls of coronary arteries may lead to stenosis or blockages.
Lumen
The inner space of blood vessels where blood flows. Changes in lumen size or shape may indicate narrowing or blockage.
Non-Calcified Plaque
Plaques that lack calcium are typically softer and more prone to instability.
Calcified Plaque
Plaques containing calcium are usually indicative of chronic coronary artery disease.
Aneurysm
Abnormal enlargement of an artery wall carries a risk of rupture.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
A condition where coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked due to plaques and stenosis.
Ejection Fraction (EF)
The percentage of blood pumped out of the left ventricle with each heartbeat indicates the heart’s pumping efficiency.
Myocardial Perfusion
CT scanning with contrast injection can assess blood flow to the heart muscle.
By mastering these terms, physicians can ensure precise evaluation of a patient’s heart and arteries, leading to well-informed treatment decisions.
Understanding these cardiac terms is just the first step. For personalized interpretation of your specific findings and their clinical significance, expert cardiac imaging consultation can translate complex medical terminology into actionable health guidance.
📄 Not Sure What Those CT Terms Actually Look Like in a Report?
Learning cardiac CT terminology is great—but seeing how it’s used in real reports is even better. Visit this CT Scan Report Format Guide to explore sample reports and better understand how findings like plaque, stenosis, or calcium scores are presented in clinical documentation.
Next Steps After Receiving Cardiac CT Results
After receiving cardiac CT scan results, consulting with a cardiologist is the essential next step. During this stage, the specialist thoroughly reviews the scan results, explaining the condition of the arteries, heart function, and any detected abnormalities. Based on the findings, various treatment recommendations may be provided:
- Lifestyle Changes: If issues like arterial blockages or other abnormalities are identified, your doctor may suggest lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, increased physical activity, or medication use.
- Advanced Treatments: Specific treatments such as angioplasty or heart surgery might be recommended for severe conditions.
- Preventive Guidance: If the results are normal, the physician can advise on preventive measures to maintain heart health.
Cardiac CT interpretation requires specialized expertise in cardiovascular imaging. If you want to ensure you fully understand your heart CT findings or need a second opinion on your cardiac health status, professional radiological consultation can provide detailed insights into your cardiovascular condition and help guide your treatment decisions.
📄 Want an Expert Radiologist to Review Your Heart CT Scan?
If you’re unsure how to interpret your cardiac CT findings, our specialized online cardiac CT interpretation service for comprehensive cardiovascular analysis—or need a second opinion—AI-PACS’s Online Reporting Services offer remote access to expert radiologists. Get accurate, timely analysis and reduce unnecessary stress with professional support tailored to your case.
Final Thoughts
Interpreting Heart CT Scan Results provides a detailed assessment of coronary arteries and heart structures, ensuring comprehensive insights for accurate diagnosis and management. This method delivers essential insights into coronary health, supporting accurate diagnoses and effective treatment planning without invasive procedures.
Becoming familiar with these terms helps patients take an active role in understanding and managing their heart health. The insights gained through these scans enable specialists to make more accurate and effective treatment decisions. A meticulous interpretation of cardiac CT scans plays a critical role in preventing severe heart complications and enhancing patient outcomes.
💡 Have you recently had a CT scan?
Get a Professional Second Opinion from Expert Radiologists.
References: