Reading Pregnancy Doppler Ultrasound
Pregnancy Doppler ultrasound is an imaging technique used to assess blood flow in the fetus’s vessels, placenta, and umbilical cord. Utilizing sound waves, this type of ultrasound measures the speed and pattern of blood flow in the vessels of both the fetus and the mother. Reading pregnancy Doppler ultrasound results is essential for understanding the following key benefits:
- Assessing Fetal Health: This ultrasound helps doctors ensure the fetus receives sufficient oxygen and nutrients through the placenta.
- Detecting Blood Flow Issues: If there are problems with blood flow in the umbilical cord or other vessels, Doppler ultrasound can identify these issues, enabling timely interventions.
- Preventing Pregnancy Complications: It is instrumental in the early detection of complications such as preeclampsia (high blood pressure during pregnancy), intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), and placental abnormalities.
- Ensuring Placental Health: The functionality of the placenta and blood flow within it are evaluated, which is critical for the fetus’s proper development.
By reading pregnancy Doppler ultrasound findings, healthcare providers can ensure a healthier pregnancy and timely interventions when needed.
Differences Between Doppler and Regular Pregnancy Ultrasound
Doppler and regular ultrasounds have distinct purposes and applications:
Regular Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the fetus and uterine organs. It is primarily used to monitor fetal growth, structure, and detect abnormalities.
Doppler Ultrasound: In addition to imaging, it measures blood flow in the fetus’s vessels, placenta, and umbilical cord. It is used to evaluate oxygen delivery and detect blood flow issues such as preeclampsia or IUGR.
In summary, regular ultrasound focuses on structural evaluation, while Doppler ultrasound assesses blood flow. If you want to know about the second trimester ultrasound and understand more, you can click on it.
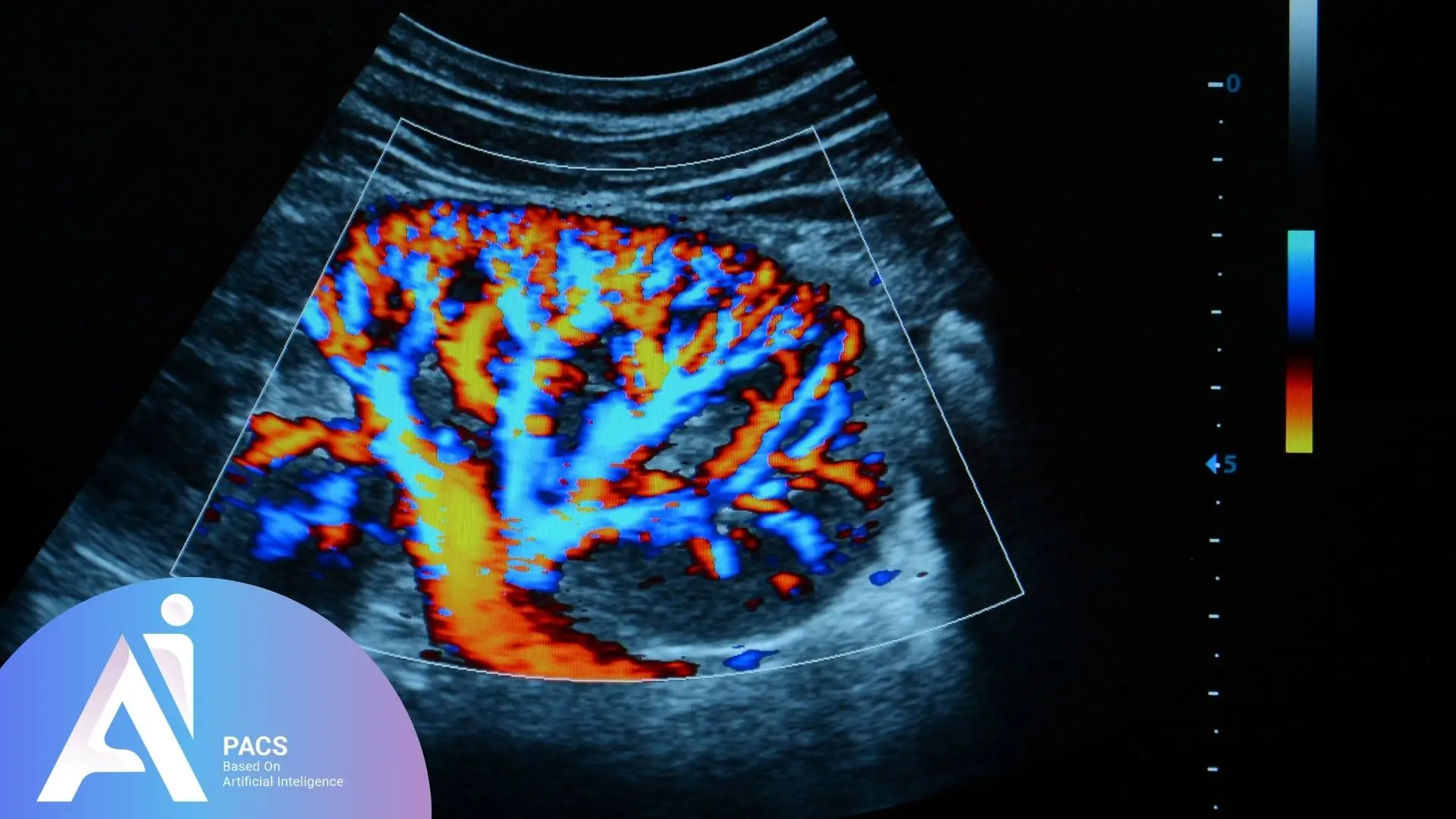
When Is Doppler Ultrasound Recommended During Pregnancy?
Doppler ultrasound is recommended when the physician suspects blood flow issues in the placenta, umbilical cord, or fetal vessels. It is commonly used in high-risk pregnancies or specific complications, such as:
- Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR): When the fetus is not growing adequately, Doppler ultrasound evaluates blood flow to the fetus.
- Preeclampsia: To assess blood flow in the placenta and fetus in pregnancies with high blood pressure.
- Multiple Pregnancies: Particularly when one or more fetuses have growth restrictions or placental issues.
- Placental or Umbilical Cord Problems: To examine the blood supply in the placenta and umbilical cord, which can affect fetal growth.
- Previous Pregnancy Issues: For mothers with a history of fetal growth problems, preterm birth, or preeclampsia.
- Maternal Diabetes or Chronic Conditions: To ensure adequate oxygen and nutrient supply to the fetus.

Specialized Terminology
Resistance Index (RI)
A ratio indicating the resistance of blood flow in fetal or maternal vessels. It is commonly used to assess blood flow in the umbilical cord and placental arteries. High RI values may indicate increased resistance in the placenta, reducing blood supply to the fetus.
Pulsatility Index (PI)
A ratio reflecting the variation in blood flow velocity with each heartbeat. It is used to evaluate placental function and fetal blood flow. High PI values may signify blood flow issues.
Systolic to Diastolic Ratio (S/D)
The ratio of blood flow velocity during the heart’s contraction phase (systole) to its relaxation phase (diastole). Abnormal increases or decreases in this ratio may indicate placental or umbilical cord issues.
Systolic Phase
The heart contraction phase when blood flow in the fetal vessels reaches its peak velocity. This phase is critical for assessing blood flow strength.
Diastolic Phase
The heart relaxation phase when blood flow in the vessels decreases. In Doppler ultrasound, the presence of diastolic blood flow is essential for ensuring healthy fetal blood circulation.
Absent End-Diastolic Flow (AEDF)
A condition where blood flow during the diastolic phase (heart relaxation) is completely absent. This may indicate severe blood supply issues to the fetus and requires immediate medical intervention.
Reversed End-Diastolic Flow (REDF)
A condition where blood flow during the diastolic phase reverses. This is a severe indicator of placental dysfunction and poses significant risks to the fetus’s health.
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) Doppler
Measures blood flow in the fetal middle cerebral artery to assess oxygen delivery to the brain. This is used when there is suspicion of reduced oxygen supply to the fetal brain.
Uterine Artery Doppler
Evaluates blood flow in the maternal uterine arteries. It is helpful in diagnosing preeclampsia and placental blood flow issues.
Umbilical Artery Doppler
Examines blood flow in the umbilical cord to evaluate fetal nutrition and oxygenation.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, pregnancy Doppler ultrasound is a vital tool for evaluating blood flow and the health of the fetus and placenta. It aids in detecting blood flow-related issues and preventing pregnancy complications, especially in high-risk pregnancies. Understanding the specialized terms and concepts associated with this ultrasound helps both mothers and physicians gain a clearer picture of the fetus’s health and take necessary measures for optimal care.
References:
fetalmedicine.org