BIRADS Categories (0-6) in Mammography
The Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BIRADS) is a standardized classification system used to describe mammography results and other breast imaging modalities. These include ultrasound and MRI, which help ensure accurate diagnosis and effective communication among medical professionals. This system was developed by the American College of Radiology (ACR) to ensure consistent reporting and interpretation of breast imaging findings, facilitating better communication among radiologists and physicians and improving decision-making for patient management.
Have a mammogram report and want to understand your BIRADS score? Upload your report to AI-PACS for a professional explanation and second opinion.
What Does BIRADS 0 Mean?
This category indicates that the imaging performed is incomplete and insufficient for a conclusive diagnosis. Additional imaging, such as extra mammographic views or supplementary tests, is required for further evaluation.
Next step: Further imaging to complete the evaluation.
What Does BIRADS 1 Mean?
A negative result, meaning that no abnormalities or signs of breast cancer are detected. The breast tissue appears entirely normal.
Next step: Continue routine screening, usually every 1–2 years depending on your age and risk level.
What Does BIRADS 2 Mean?
This category includes benign findings that do not require further investigation. Common benign findings include cysts, fibroadenomas, and other non-cancerous abnormalities.
Next step: Routine screening; no additional testing required.
What Does BIRADS 3 Mean?
Findings in this category are most likely benign, with a greater than 98% probability of being non-cancerous. Follow-up imaging is recommended to ensure that no subtle changes occur over time, as rare cases of malignancy may still develop or small abnormalities may become more evident in subsequent screenings. Typically, a short-term follow-up mammogram is advised within 6 months to monitor any potential changes.
Next step: Schedule follow-up imaging to monitor for any changes.
What Does BIRADS 4 Mean?
This category includes findings that are suspicious for malignancy, warranting a biopsy for further evaluation. BIRADS 4 is subdivided into three levels of malignancy risk:
- 4A: Low suspicion (2-10%)
- 4B: Moderate suspicion (10-50%)
- 4C: High suspicion (50-95%)
Next step: A biopsy is performed to confirm the presence or absence of cancer.
What Does BIRADS 5 Mean?
Findings in this category are highly suggestive of malignancy, with a greater than 95% probability of breast cancer. A biopsy is strongly recommended.
Next step: A biopsy is urgent, and cancer treatment planning begins.
What Does BIRADS 6 Mean?
This category applies to cases where breast cancer has already been confirmed through a biopsy. Imaging is used to monitor the disease and evaluate treatment response.
Next step: Ongoing imaging as part of your treatment plan.
The Importance of BIRADS Classification
Standardized Reporting
BIRADS provides a structured approach for reporting mammography and other breast imaging results, ensuring consistency in diagnosis and facilitating early detection of breast cancer. This standardization helps physicians make more accurate treatment decisions, improves patient outcomes, and minimizes diagnostic errors by reducing false positives and negatives. It also ensures uniformity and clarity in communication among radiologists and physicians, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.
Enhanced Medical Communication
The classification system facilitates better interdisciplinary communication between radiologists and treating physicians. Using well-defined categories allows for precise and clear reporting, enabling seamless information exchange and improving medical decision-making.
More Accurate Treatment Decisions
By categorizing breast findings based on the likelihood of malignancy, BIRADS assists physicians in determining the need for further tests, monitoring, or immediate treatment. For example, a BIRADS 3 classification typically requires short-term follow-up imaging, while a BIRADS 4 or 5 finding necessitates a biopsy to confirm malignancy and guide treatment decisions. It helps healthcare providers adopt the most appropriate approach based on the risk assessment of each case.
Reducing Patient Anxiety
A clear and structured BIRADS report helps reduce anxiety among patients. Those with benign or normal findings can be reassured, while those requiring further evaluation can proceed with well-defined steps for timely diagnosis and management.
If you want to explore how BIRADS compares with other imaging systems, visit Breast MRI: Why, When, Who? A Patient’s Journey in Breast Cancer Screening. You can also learn more about Understanding Calcifications in Mammography to better interpret what those findings mean in your report.
Effective Patient Follow-Up
BIRADS plays a crucial role in establishing appropriate follow-up protocols. For instance, in BIRADS 3 cases, where lesions are likely benign but require monitoring, a follow-up mammogram is usually recommended in 6 months. This systematic approach improves early detection and intervention.
Minimizing Diagnostic Errors
By using standardized categories with clear diagnostic criteria, BIRADS reduces false-positive and false-negative errors. This enhances diagnostic reliability and improves patient outcomes.
Comparison with Other Classification Systems
While BIRADS is widely used for breast imaging, other classification systems like the TNM staging system focus on cancer progression and metastasis. Unlike TNM, which is primarily used for staging confirmed cancers, BIRADS aids in risk stratification and early detection. This distinction makes BIRADS particularly valuable for screening programs and preventive care. In short, BIRADS is about early detection; TNM is about disease staging.
Supporting Research and Education
As a universal classification system, BIRADS serves as an important tool for clinical research and medical education. Standardized data collection enables researchers to analyze trends, improve diagnostic techniques, and advance breast cancer detection and treatment strategies.
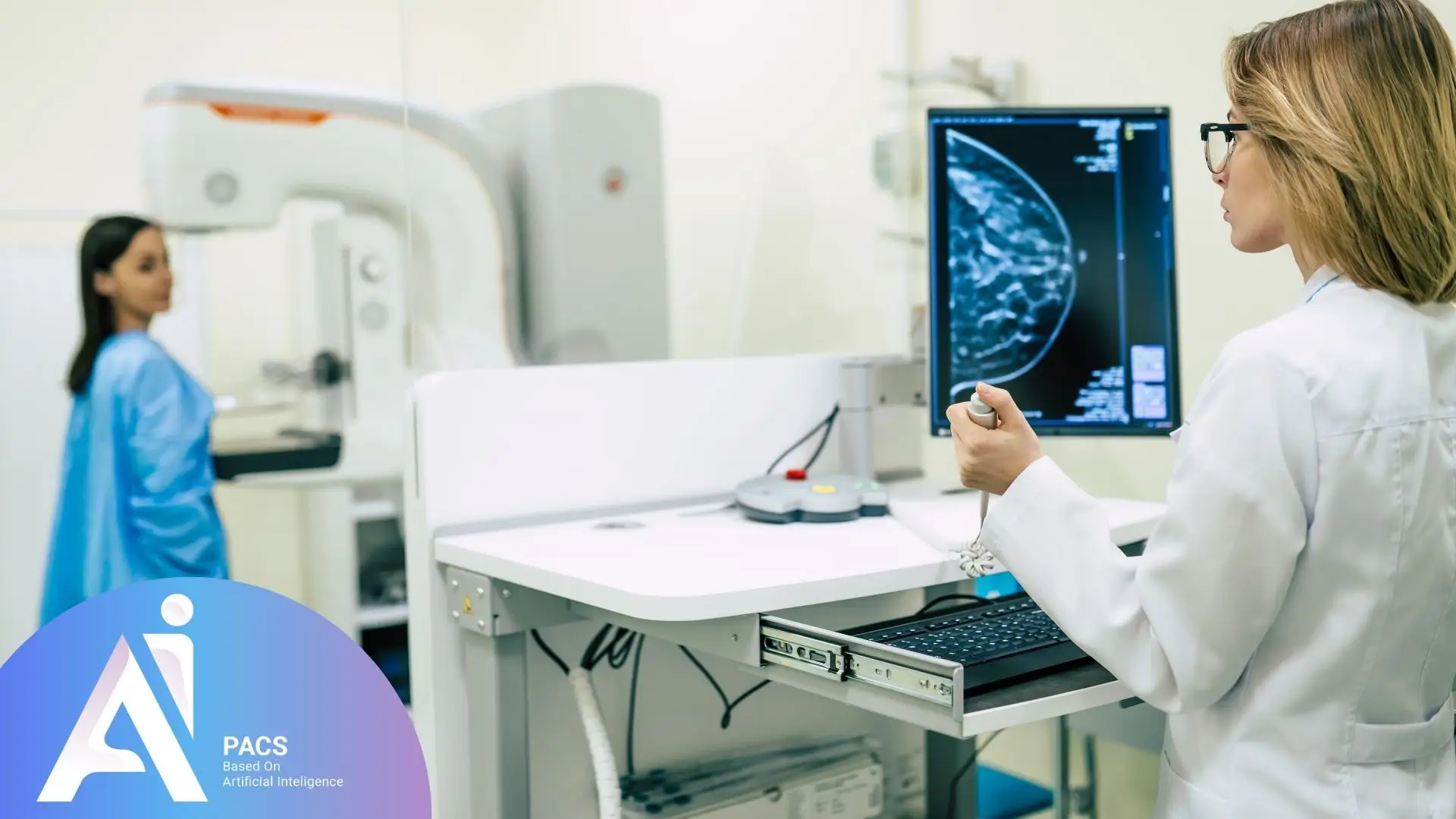
Additional Imaging and Tests
When mammography findings are inconclusive or suspicious, additional imaging techniques such as breast ultrasound or MRI may be recommended for further assessment:
- Breast Ultrasound is particularly useful for distinguishing between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts. It helps detect abnormalities that may not be clearly visible on mammography, especially in women with dense breast tissue.
- Breast MRI is a highly sensitive imaging method used for evaluating tissue abnormalities and detecting tumors. It is particularly beneficial for women at high risk of breast cancer or those with dense breast tissue, providing more detailed insights.
- Biopsy is performed when an imaging study suggests a high suspicion of malignancy (BIRADS 4 or 5). It involves removing a small tissue sample from the abnormal area for microscopic examination to confirm or rule out cancer.
Final Thoughts
The BIRADS system plays a crucial role in breast cancer detection, diagnosis, and management. Compared to other classification systems like the TNM staging system used for cancer progression assessment, BIRADS focuses on imaging-based categorization, making it particularly useful for early detection and risk stratification. By offering a standardized, precise approach to reporting mammography findings, BIRADS improves communication among medical professionals, enhances patient follow-up, and supports early cancer detection. It helps reduce diagnostic errors, lower patient anxiety, and promote more effective treatment decisions, ultimately contributing to better breast health and improved patient care.
Your breast health journey deserves clarity and confidence. 👉 Upload your mammography or breast MRI report to AI-PACS now for a detailed second opinion from expert radiologists and explore more guides like Breast MRI and Early Detection of Breast Cancer or Reading and Interpreting Mammography to understand your results more deeply.
References: